XB-IMG-122534
Xenbase Image ID: 122534
|
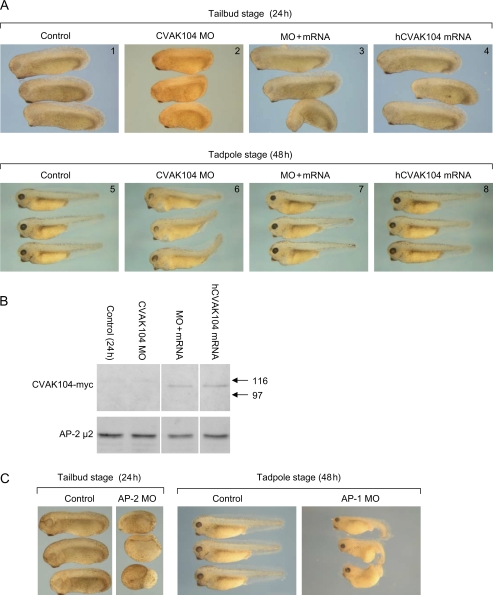
Figure 6. CVAK104 knockdown and rescue in Xenopus.A) Fertilized X. tropicalis eggs were injected with a control MO (panels 1 and 5) or a MO against CVAK104 (panels 2 and 6) at the one-cell stage and imaged either 24 h or 48 h post-fertilization. To rescue the knockdown phenotype, fertilized eggs were injected with anti-CVAK104 MO + mRNA encoding human CVAK104-myc (panels 3 and 7), then imaged either 24 h or 48 h post-fertilization. Expression of human CVAK104-myc resulted in high levels of rescue both at tailbud and tadpole stages. Expression of human CVAK104-myc alone had no apparent detrimental effects (panels 4 and 8). B) Western blots of extracts from 24 h embryos were probed with anti-myc antibody. AP-2 μ2 was included as a loading control. Human CVAK104-myc was detectable in embryos that had been injected with mRNA. C) Fertilized eggs were injected with either a control MO, a MO against AP-2 μ2, or a MO against AP-1 μ1A, then imaged either 24 h or 48 h post-fertilization. Both knockdowns cause severe phenotypes, but the AP-1 knockdown phenotype is more similar to the CVAK104 knockdown phenotype. Image published in: Borner GH et al. (2007) Image downloaded from an Open Access article in PubMed Central. © 2007 The Authors Journal compilation © 2007 Blackwell Publishing Ltd Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
