XB-IMG-124440
Xenbase Image ID: 124440
|
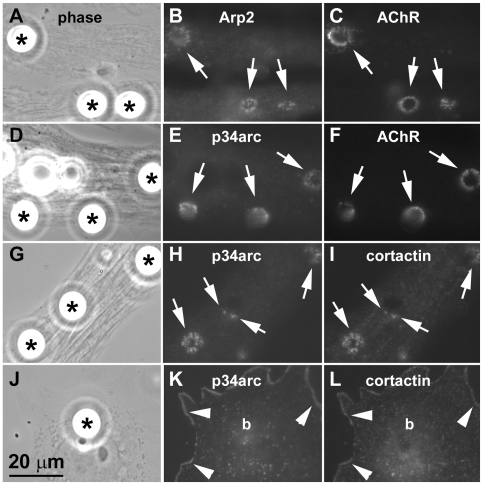
Figure 1. Localization of Arp2/3 complex proteins and cortactin at AChR clustering sites.Cultured embryonic Xenopus muscle cells labeled with rhodamine-α-bungarotoxin (R-BTX) were stimulated overnight with polystyrene beads coated with heparan-binding growth-associated molecule (HB-GAM) (A, D; asterisks) to induce AChR clusters (C, F). Cells were then fixed and labeled with affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies against the Arp2/3 complex proteins Arp2 (B) and p34arc (E) followed by FITC-linked anti-rabbit secondary antibodies. Separately, bead-stimulated muscle cells (G) were labeled with anti-p34arc polyclonal (H) and anti-cortactin monoclonal (I; mAb4F11) antibodies and then FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit and rhodamine-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibodies. AChRs, Arp2 and p34arc were clustered at bead-muscle contacts (A-F; arrows) where cortactin localized and overlapped in distribution with p34arc (H and I; arrows). In primary muscle cultures non-muscle cells were occasionally found (J) and in these cells p34arc (K) and cortactin (L) localized along the cell periphery (arrowheads) but were not clustered at bead-cell contacts (“b” in K and L corresponds to bead indicated by asterisk in J). Image published in: Madhavan R et al. (2009) Madhavan et al. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
