XB-IMG-125040
Xenbase Image ID: 125040
|
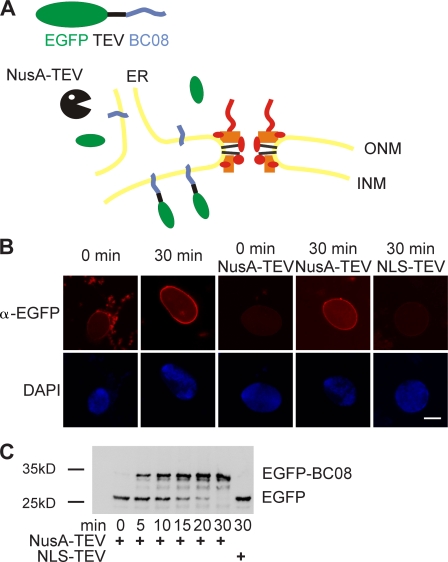
Figure 5. An assay for the transport of membrane proteins to the INM. (A) Schematic representation of the assay. The transmembrane-containing INM protein BC08 is fused to an EGFP domain followed by a recognition site for the TEV protease (top). The fusion protein is reconstituted into liposomes that rapidly fuse with the ER and ONM in the nuclear assembly reaction. INM localization of the reporter can be distinguished from ONM and ER localization by the reporter’s protection from TEV protease fused with a large NusA domain to prevent its diffusion through the NPC. (B) Nuclei were assembled in Xenopus egg extracts. After 50 min, i.e., when a closed NE had formed, proteoliposomes containing the reporter were added. At the indicated time points, buffer, NusA-fused TEV protease, or TEV protease linked to NLS peptides was added. Protease cleavage was stopped after 5 min by fixation, and samples were processed for immunofluorescence and analyzed by confocal microscopy. α-EGFP immunofluorescence is shown in red, and DAPI is shown in blue. (C) Reactions were performed as in B. Protease cleavage was stopped by the addition of SDS sample buffer and boiling. Protease protection of the reporter was analyzed by Western blotting with the position of the uncleaved (EGFP-BC08) and the cleaved reporter with only the EGFP visible indicated. Bar, 20 µm. Image published in: Theerthagiri G et al. (2010) © 2010 Theerthagiri et al. This image is reproduced with permission of the journal and the copyright holder. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
