XB-IMG-127223
Xenbase Image ID: 127223
|
|
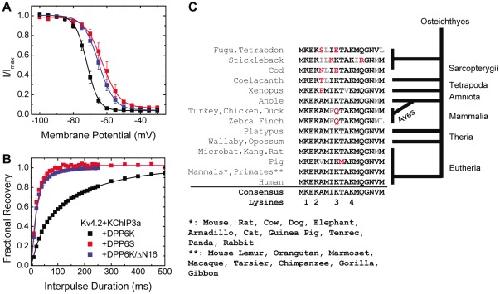
Figure 4. The DPP6K variable N-terminus is responsible for its distinct functional effects.(A) Voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation of ternary complex containing DPP6K and DPP6K/ΔN16 deletion mutant. The protocol was the same as that of Fig. 2B. (B) The kinetics of recovery from inactivation at −100 mV. The protocol was the same as that of Fig. 3. (C) Alignment of amino acid sequences of DPP6K variable N-terminus from various organisms. Consensus residues are shown in black; conservative substitutions, in gray; non-conservative substitutions, in red. Major evolutionary branch points indicated along the alignment relative to a terminus in placental mammals. Image published in: Jerng HH and Pfaffinger PJ (2012) Jerng, Pfaffinger. This image is reproduced with permission of the journal and the copyright holder. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
