XB-IMG-134810
Xenbase Image ID: 134810
|
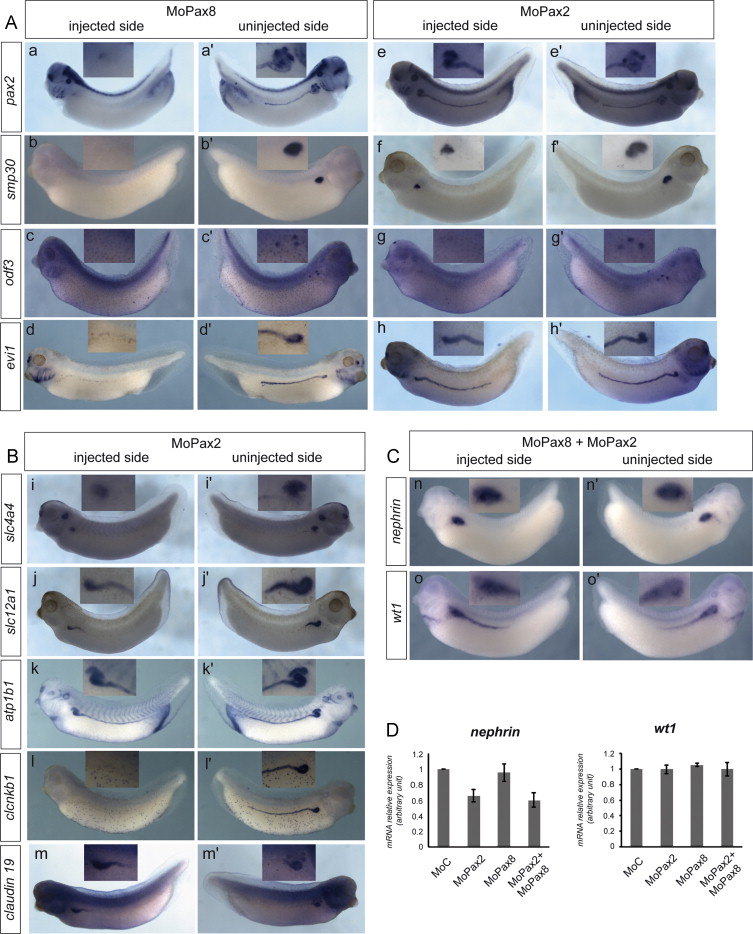
Fig. 2. Pax 8 and Pax2 loss of function differentially affects tubule but not glomus marker genes expression at late tailbud stage. (A, B) Whole mount in situ hybridization for tubule marker genes. Embryos were injected with MoPax8 (aâd) or MoPax2 (eâm) at the 4-cell stage, in the equatorial region of both left blastomeres. They were cultured until the tailbud stage 33â35, fixed and analyzed by in situ hybridization with specific probes for the indicated genes. For each embryo, injected (aâm) and uninjected (a׳âm׳) sides are shown. Pax8 depletion prevents expression of marker genes all along the entire tubule expression domain. In Pax2 morphants, gene expression in the proximal part of the tubule, including nephrostomes, is affected. Expression in the distal tubule is not modified by the MoPax2 except for the terminal differentiation marker clcnkb1 whose expression is completely inhibited. Insets show higher magnification of the anterior pronephric territory. (C) Whole mount in situ hybridization for the glomus marker genes wt1 and nephrin. Embryos were injected with a mixture of MoPax8 and MoPax2 in the equatorial region of both left blastomeres at the 4-cell stage and cultured until the tailbud stage 33. Injected sides are shown in (n, o), uninjected sides in (n׳, o׳). Insets show higher magnification of the anterior pronephric territory. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of wt1 and nephrin. Embryos were injected with the indicated Mo at the 4-cell stage in all four blastomeres. They were cultured until the late tailbud stage 33 and processed for RT-qPCR analysis. Average values from three independent experiments. Neither MoPax2 nor MoPax8 injected alone or together significantly affects wt1 and nephrin expression compared to the control (MoC). Image published in: Buisson I et al. (2015) Copyright © 2015. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
