XB-IMG-144775
Xenbase Image ID: 144775
|
|
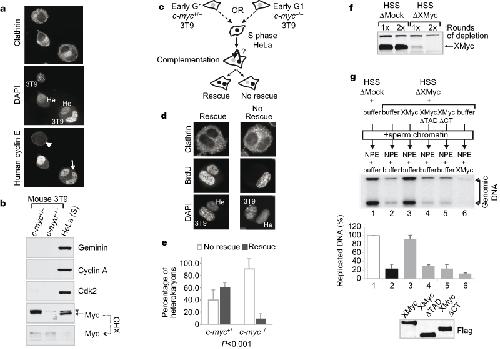
Figure 3: Myc is required for efficient DNA replication and proper origin specification in the absence of transcription. a, Cyclin/Cdk shuttles within human/mouse heterokaryons. Isolated heterokaryons were stained with a human-specific antibody against cyclin E. Arrow, 3T9 mouse nuclei within the heterokaryons uptaking cyclin E; arrowhead, isolated 3T9 cells, devoid of cyclin E. Mouse (3T9) and human (He) nuclei exhibit distinct 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining patterns. b, Western blot analysis of selected proteins in whole-cell lysates from the indicated cells before cell fusion. CHX, cycloheximide; asterisk, nonspecific band in HeLa cells. c, Experimental scheme for the cell fusion experiments (see also Supplementary Information). d, Representative images of heterokaryons identified in the screen for replication rescue, summarized in e. e, Average of cell fusion experiments. More than 70 heterokaryons were counted and classified according to the patterns shown in d. The P value (χ2 analysis) is shown below. Error bars indicate s.d. f, Western blot analysis of mock- or XMyc-depleted Xenopus cell-free extracts. g, Replication assay in the Xenopus HSS/NPE system. Genomic DNA was extracted at 90 min and incorporated 32P was quantified by PhosphorImager. Recombinant XMyc proteins (50 nM) were added to XMyc-depleted HSS extracts (lanes 3–5) or to NPE (lane 6) as indicated. A representative autoradiograph is shown. An average of three experiments is shown in the graph below. Error bars indicate s.d. Bottom panel: western blot analysis of recombinant XMyc protein levels. Image published in: Dominguez-Sola D et al. (2007) Copyright © 2007. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Macmillan Publishers Ltd. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
