XB-IMG-148471
Xenbase Image ID: 148471
|
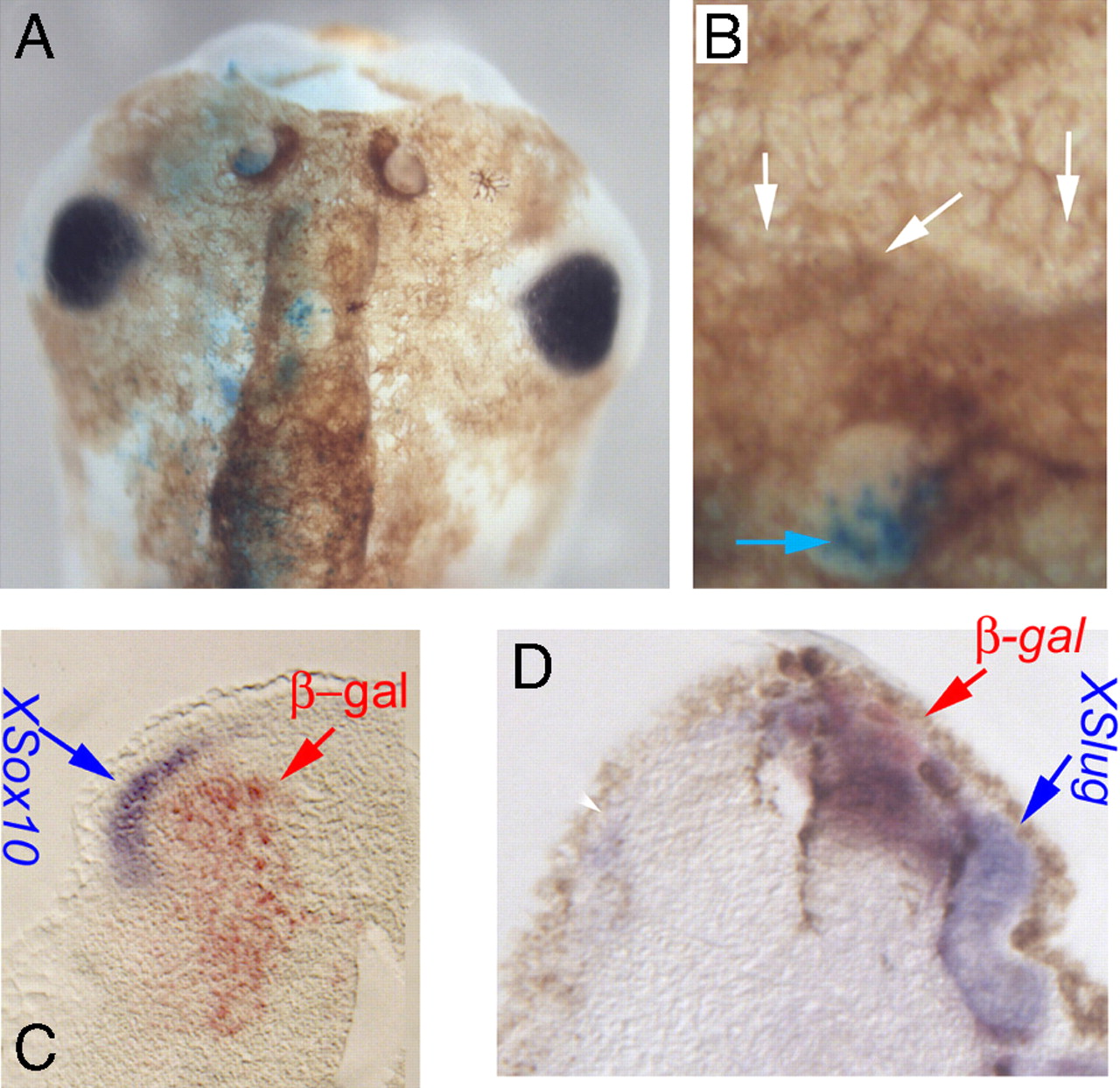
Fig. 4. KCNE1-induced hyperpigmentation phenotype is a non-cell-autonomous effect involving up-regulation of Sox10 and Slug expression. (A) Embryos were injected with a mixture of KCNE1 and β-gal mRNAs and were lightly bleached at stage 43, allowing evaluation of melanocytes and clear detection of the β-gal lineage label in the area dorsal to the eyes, which normally has few or no melanocytes (all of the melanocytes in this region are ectopic). The vast majority of the excess cells did not themselves contain the lineage label (B, white arrows indicate lack of β-gal signal; blue arrow indicates cells positive for β-gal), illustrating the non-cell-autonomous mechanism of hyperpigmentation induction by KCNE1. Embryos were injected with KCNE1 + β-gal mRNAs at the one-cell stage (resulting in mosaic expression throughout the embryo), processed for in situ hybridization, and sectioned. Note the ectopic expression of Sox10 (C) and Xslug (D, compare with contralateral side showing very little Sox10 expression on the side where KCNE1 was not injected). Ectopic domains lie adjacent to KCNE1-misexpressing cells. Red signal (and red arrowheads) indicate β-gal lineage label of injected cells. Blue arrows indicate the positive in situ hybridization signal (purple). Image published in: Morokuma J et al. (2008) Copyright © 2008. Image reproduced with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
