XB-IMG-148640
Xenbase Image ID: 148640
|
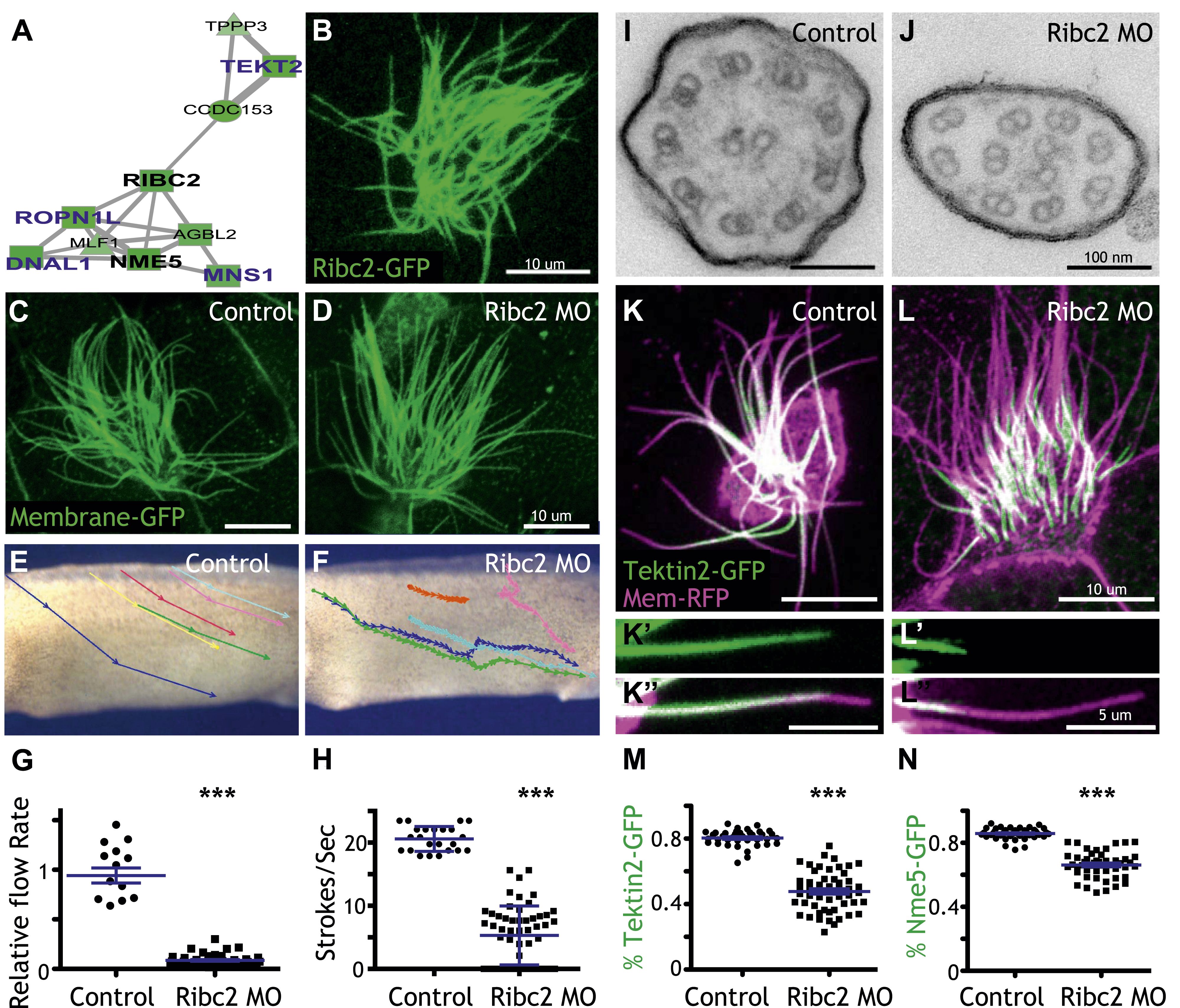
Figure 4. Ribc2 is required for ciliary motility.
(A) Ribc2 is clustered in HumanNet with known ciliary beating components, such as Dnal1, Ropn1l, and Mns1 (B) Ribc2-GFP is localized along the axoneme. (C) An MCC of a stage 27 control embryo injected with membrane-GFP. (D) An MCC of a stage 27 embryo injected with Ribc2 morpholino. Ribc2 is not essential for cilia assembly. Tracking of latex beads moving across the epidermis of the control embryo (E) and the Ribc2 morphant (F). An arrow represents the moving distance per time frame. The relative average flow rate is shown in (G). While the average flow rate of control is normalized to 1 ± 0.075 (mean ±SEM), it is significantly reduced to 0.085 ± 0.008 in Ribc2 morphants. (H) Quantification of ciliary beating using high-speed confocal (Videos 3 and 4). Beat frequency is 20.59 ± 0.410 strokes/s in control whereas only 5.29 ± 0.635 strokes/s following Ribc2 knockdown. Ultrastructure of axoneme from a control embryo (I) and a Ribc2 knockdown embryo (J) were visualized using TEM. Lack of dynein arms were observed in Ribc2 morphants. (K) A MCC of a stage 27 control embryo injected with Tektin2-GFP and membrane-RFP. Enlarged view of an axoneme is shown in (K′) (K′′). (L) A MCC of a stage 27 Ribc2 morphant. Enlarged view is shown in (L′) (L′′). (M) Tektin2-GFP generally decorates 80% (±0.8) of the axoneme as marked by membrane-RFP; this ratio is significantly reduced, to 48% (±1.6), following Ribc2 knockdown (N). Nme5-GFP generally decorates 86% (±0.5) of the axoneme; this ratio is significantly reduced, to 66% (±1.2), following Ribc2 knockdown. ***p < 0.0001 Mann–Whitney test.
Image published in: Chung MI et al. (2014) Copyright © 2013, Chung et al. This image is reproduced with permission of the journal and the copyright holder. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
