XB-IMG-150926
Xenbase Image ID: 150926
|
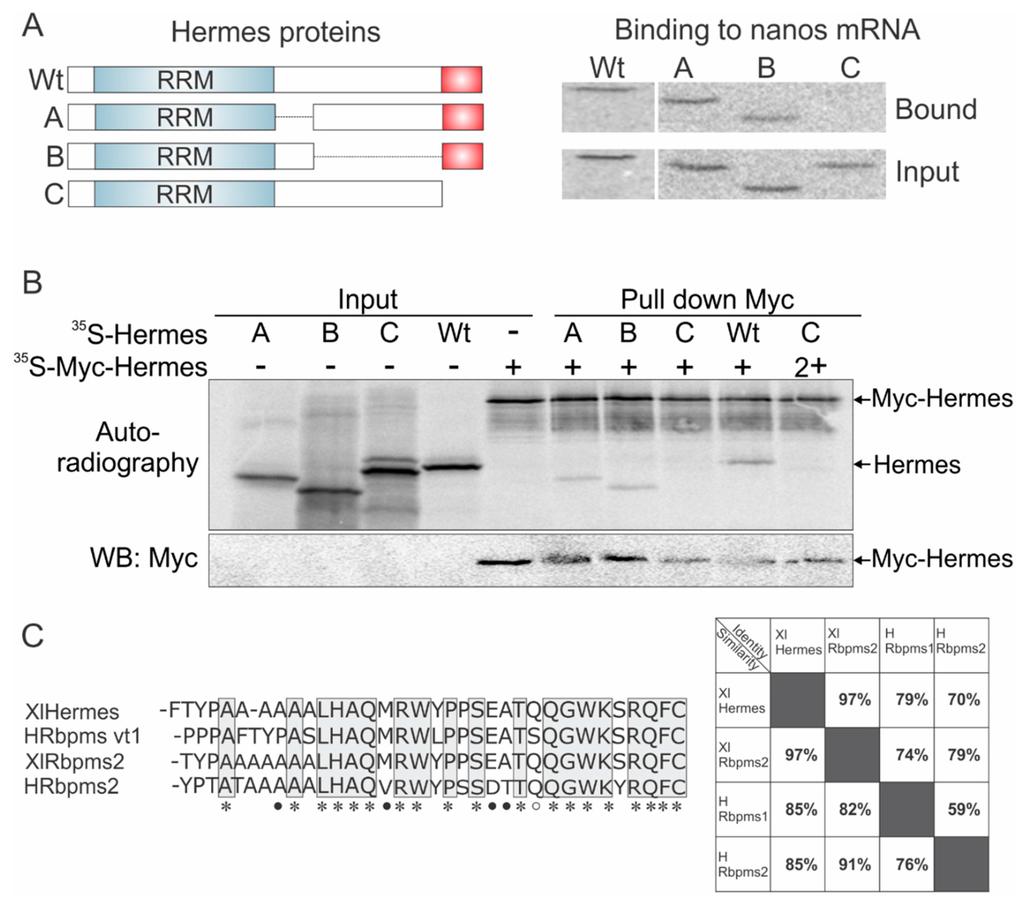
Figure 3. The carboxyl terminal 34 amino acids of Hermes/Rbpms are required for nanos1 binding and for Hermes/Rbpms dimerization. (A) Three deletion mutants of Hermes/Rbpms are diagramed showing the RRM domain and the hydrophilic carboxyl terminal 34 amino acids (red box). 35S-methionine labeled Hermes/Rbpms and its deletion mutants were analyzed for their ability to be pulled-down by nanos1 3′UTR immobilized on AADA beads. Wild-type and mutant protein (input) used in reaction and bound are shown by SDS-PAGE. Note that only the last 34 amino acids were required for nanos binding in the presence of the Hermes/Rbpms RRM; (B) The presence of Hermes/Rbpms homodimers was detected by autoradiography as two bands. Note that Hermes/Rbpms missing the terminal 34 amino acids failed to form a dimer. As nanos RNA was not present, Hermes/Rbpms formed homodimers in the absence of RNA; (C) C-terminal region involved in Hermes/Rbpms homodimerization and binding to the nanos 3'UTR. Alignment of conserved terminal 34 amino acids (AA) of Human and Xenopus Hermes/Rbpms proteins. An * (asterisk) indicates a fully conserved AA. Black dots indicate conservation between groups of strongly similar properties (scoring > 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). A white dot indicates weakly similar properties (scoring ≤ 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix), Clustal Omega, EMBL-EBI, UK. Table shows the high level of identity and similarity between frog and human Hermes/Rbpms proteins. Image published in: Aguero T et al. (2016) Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. This image is reproduced with permission of the journal and the copyright holder. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
