XB-IMG-156708
Xenbase Image ID: 156708
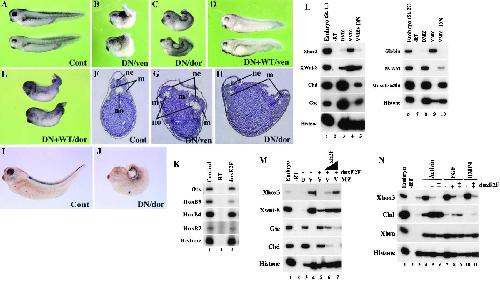
|
|
Figure 7.
Inhibition of xE2F Function Affects the Development of Ventral and Posterior Structures
Uninjected embryos are shown in (A) as a control. The dnxE2F RNA (120 pg) was injected into the ventral or dorsal side of four-cell stage embryos (B and C, respectively), and the injected embryos were developed to tadpole stages. The injected embryos showed defects in trunk and posterior regions, but not in anterior regions. The effect of dnxE2F on normal development was partially rescued by coinjection of wild-type xE2F RNA (0.5 ng) (D and E). Cont, control; DN/ven, dnxE2F RNA into ventral side; DN/dor, dnxE2F RNA into dorsal side; DN+WT/ven, dnxE2F RNA with wild-type xE2F RNA into ventral side; DN+WT/dor, dnxE2F RNA with wild-type xE2F RNA into dorsal side. (F–H) Histological section of control and dnxE2F-injected embryos. ne, neural tube; m, muscle; no, notochord. (I and J) Overexpression of dnxE2F affects the expression of the spinal cord marker HoxB9. dnxE2F RNA (120 pg) was injected into the dorsal side of four-cell stage wild-type embryos and subjected to whole-mount in situ hybridization with an antisense HoxB9 probe at tadpole stages. Anterior side of embryos is to the left. Cont, control; DN/dor, dnxE2F RNA into dorsal side. (K) Inhibition of Hox gene expression by dnxE2F. Embryos injected dorsally with dnxE2F RNA (120 pg) were developed to tailbud stage (stage 25), and two embryos each were subjected to RT-PCR analysis. (L) Inhibition of xE2F function in marginal zone explants dorsalizes ventral mesoderm. dnxE2F RNA (120 pg) was injected into the ventral side of four-cell stage embryos, and dorsal and ventral marginal zone (DMZ and VMZ) explants were excised at early gastrula stages. The explants were subjected to RT-PCR analysis at midgastrula (stage 11) and tailbud (stage 27) stages. DN, dnxE2F RNA. (M) Wild-type xE2F rescues dorsalization of ventral mesoderm caused by dnxE2F. dnxE2F RNA (120 pg) was injected with increasing amounts of wild-type xE2F RNA (2.5 ng and 5.0 ng in lanes 6 and 7, respectively). DMZ and VMZ explants are isolated at early gastrula stages and subjected to RT-PCR at midgastrula stages. MZ, marginal zone; D, dorsal; V, ventral. (N) xE2F affects mesoderm formation induced by growth factors. Xenopus embryos were injected either with 60 pg (lanes 5 and 8) or 120 pg (lanes 6, 9, and 11) dnxE2F RNA into animal poles of two-cell stage embryos. Ectodermal explants from blastulae were treated with activin (supplied as oocyte supernatant; see Experimental Procedures) or FGF (100 ng/ml) and subjected to RT-PCR analysis at early gastrula stages. For BMP4 treatments, BMP4 RNA (0.5 ng) was coinjected with dnxE2F RNA. Image published in: Suzuki A and Hemmati-Brivanlou A (2000) Copyright © 2000. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
