XB-IMG-157388
Xenbase Image ID: 157388
|
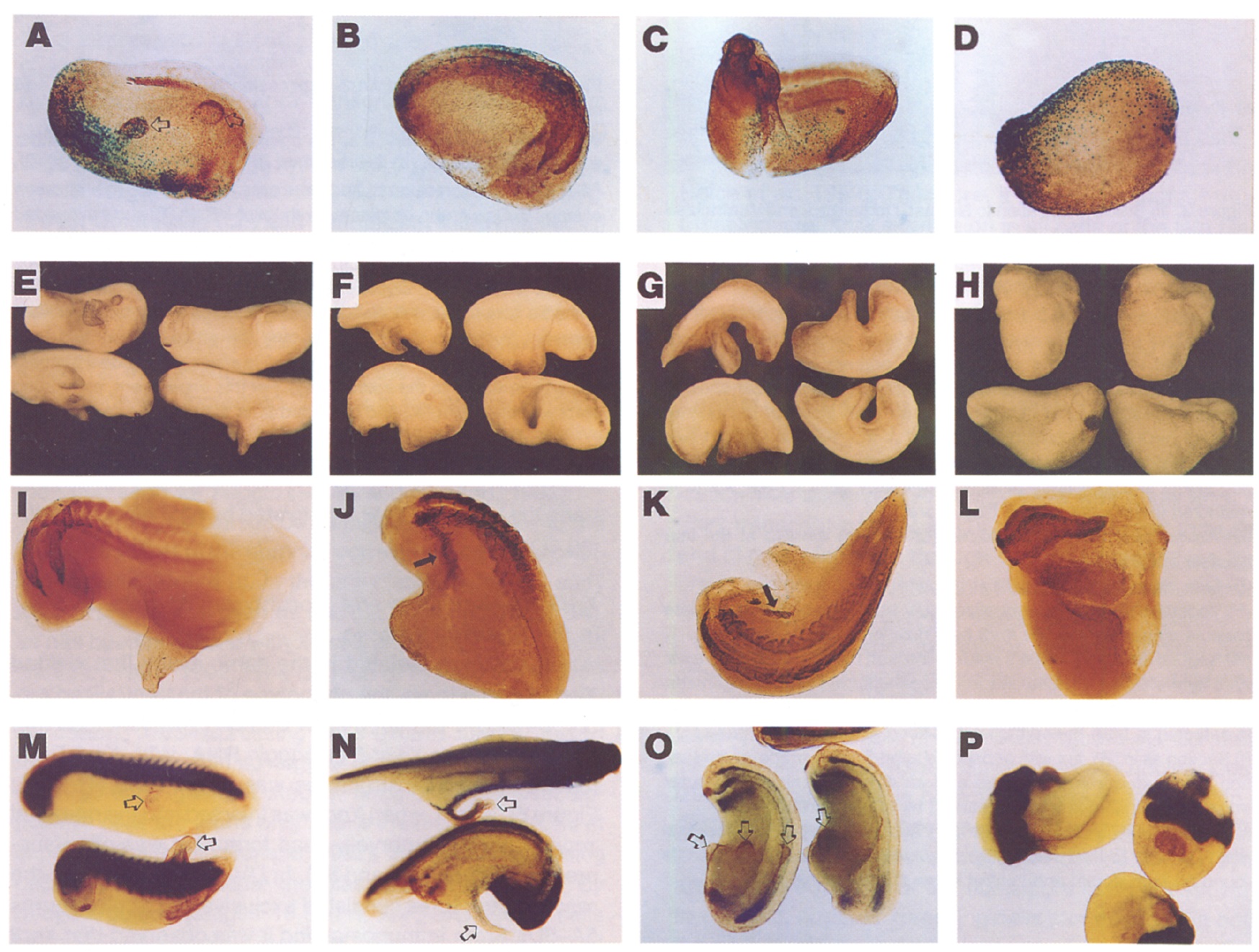
Figure 5. Effects of Xnr3 RNA Injection into Embryos
(A-D) UV-ventratlzed embryos were injected at the 32-M stage with 100 pg each of Xnr3 and 6galactosidase RNAs. Single cells were injected
at either the animal tier (A), the two marginal tiers (S), or the vegetal tier (C). In (D), the embryo was injected in the animal tier with B-galactosidase
RNA only. At about stage 25, the embryos were ftxed and stained with X-Gal and 12/101.
(E-L) Normal embryos (not UV-treated) were injected with 166 pg of Xnr3 RNA at either the animal tier (E and I), the two marginal tiers (F and
J), or the vegetal tier (0 and K). (H) and (L) show embryos injected in the marginal zone with 196 pg of noggin RNA. Embryos were fixed at about
stage 25 and were either photographed without further processing (E-H) or stained with an anti-muscle antibody (I-L). Induced ectopic patches
of muscle are marked with arrows.
(M-P) In situ hybridizations. Embryos were injected at the l-cell stage with 166 pg of Xnr3 RNA at the animal pole. Induced protrusions are marked
with open arrows. (M) Embryos stained at approximately stage 25 for collagen type II RNA expression. (N) Embryos stained at approximately
stage 35 for N-CAM and nrpl RNA. The upper embryo represents the class that stains weakly for neural markers in the protrusion; the lower
embryo shows extremely weak staining, despite the overstaining for the primary neural axis. (0) Embryos stained at approximately stage 25 for
HNF3alXFKH2 RNA. When examined in all orientations, all protrusions are negative, although edge effects and staining in the endoderm sometimes
give an impression of staining (embryo on right) (P) noggin RNA-injected embryo (160 pg; about stage 25) stained for N-CAM and nrpl RNA. Image published in: Smith WC et al. (1995) Copyright © 1995. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
