XB-IMG-168550
Xenbase Image ID: 168550
|
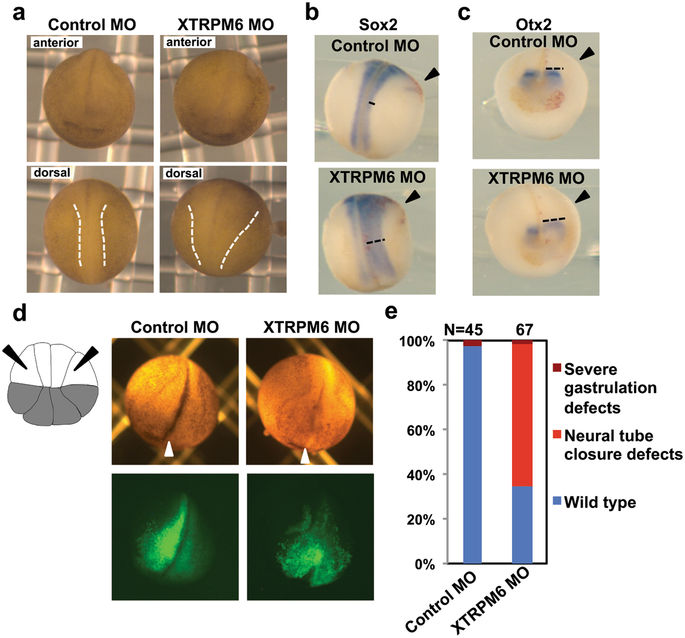
Figure 2. XTRPM6 is required for neural tube closure. (a) A control MO or XTRPM6 MO was injected into the two dorsal blastomeres at the 4-cell stage embryos. At stage 20, depletion of XTRPM6 caused neural tube closure defect. Dotted lines indicate the neural fold. (b) and (c) Visualization of the neural plate by staining with Sox2 (b) and Otx2 (c). The in situ hybridization of Sox2 (pan-neural marker) and Otx2 (pre-chordal neural plate marker) indicate that a wider neural plate is observed on the XTRPM6 MO injected side compared to that of uninjected side (black dotted lines). (d) The XTRPM6 MO or a control MO was co-injected with GFP RNA into the animal lateral blastomeres of the 16-cell embryo to target the lateral neural plate and epidermal tissue, where XTRPM6 is highly expressed. The lateral animal blastomeres are indicated with black arrows in the illustration of the 16-cell embryo. White arrowheads indicate midline of the embryo. (e) Quantification of the results from (d). The collective total number of injected embryos from all experiments is indicated above each bar. Image published in: Komiya Y et al. (2017) © The Author(s) 2017. This image is reproduced with permission of the journal and the copyright holder. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
