XB-IMG-170488
Xenbase Image ID: 170488
|
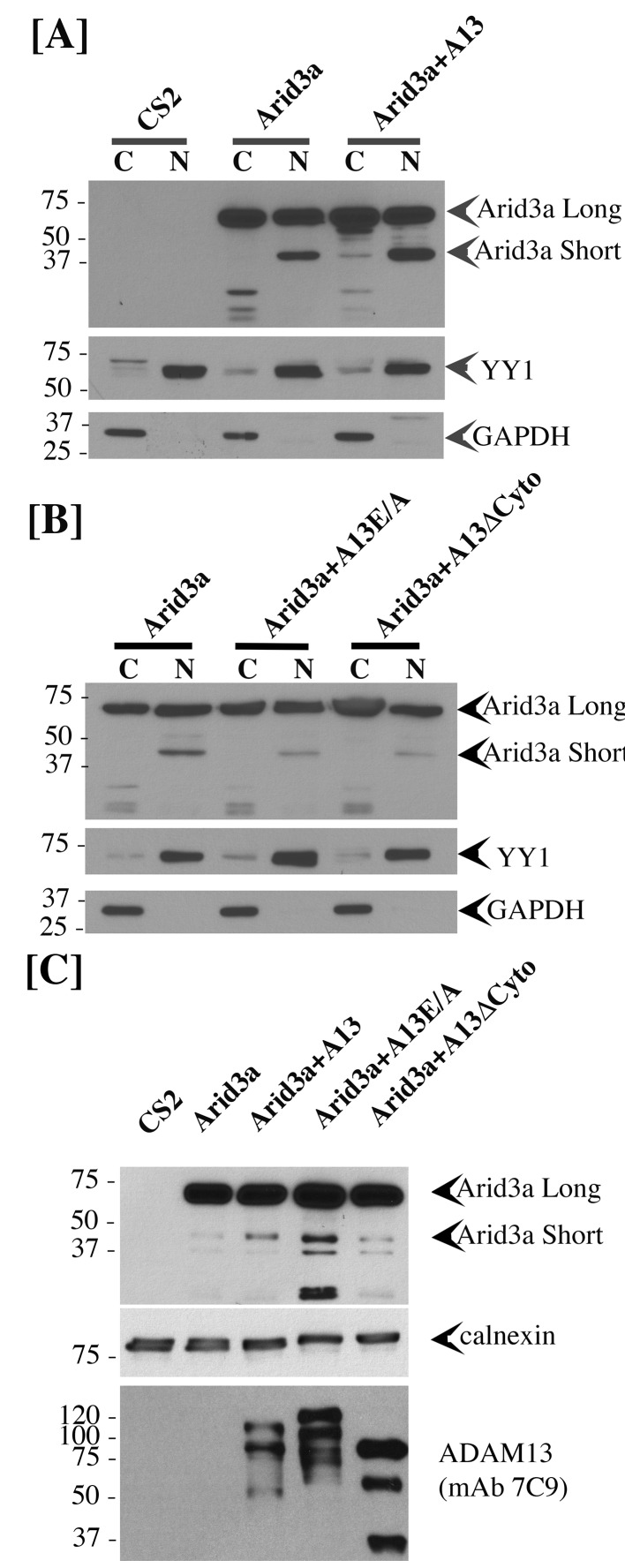
Figure 10. adam13 regulates arid3a post-translational modification.Western blot from transfected Hek293T cells. (A–B) cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) extracts from cells transfected with the empty vector (CS2), Arid3a-flag, adam13 (A13) or both. The blots were re-probed with the transcription factor YY1 as a nuclear marker and GAPDH as a cytoplasmic marker. The full-length Xenopus laevis Arid3a is detected at approximately 60 kDa (Arid3a Long). A shorter fragment is detected at about 40 kDa (Arid3a Short). (A) Co-transfection of adam13 with Arid3a increases the Arid3a protein level in the cytoplasm by 30% and the shorter fragment of Arid3a in the nucleus by five folds. (B) Co-transfection of Arid3a with the proteolytically inactive mutant adam13 (A13E/A) or the mutant lacking the cytoplasmic domain (A13ΔCyto) does not increase the shorter fragment in the nucleus. (C) Membrane extract from Hek293T cells transfected with Arid3a-flag and the adam13 constructs. Co-transfection of Arid3a with adam13 increases the intensity of the 40 kDa Arid3a fragment. This is not observed in the absence of the adam13 cytoplasmic domain. In contrast, a much more significant increase is observed when Arid3a is co-transfected with the A13E/A mutant. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
