XB-IMG-47736
Xenbase Image ID: 47736
|
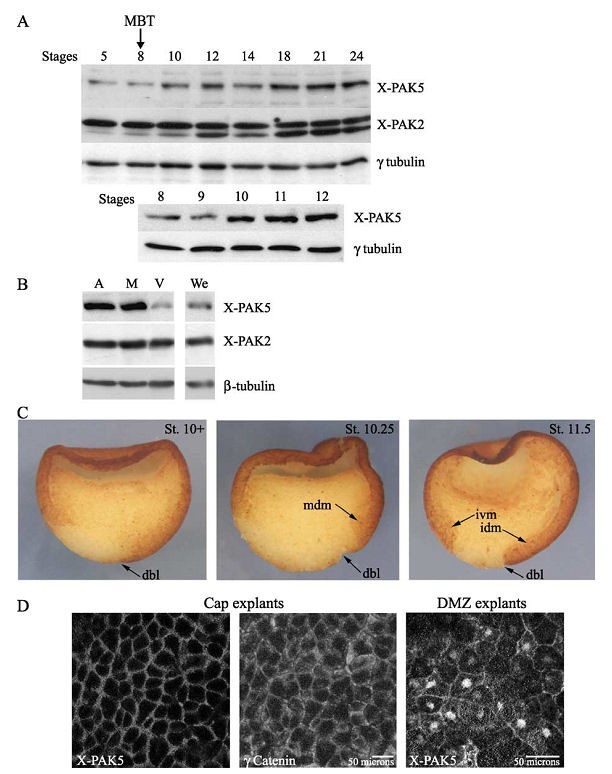
Fig. 1. Spatiotemporal expression pattern of X-PAK5 during early Xenopus development. (A) Temporal expression pattern of X-PAK5. Protein extracts from
embryos harvested at the indicated stages were subjected to Western blot analyses with anti-X-PAK5, anti-X-PAK2, and anti-g tubulin antibodies. Levels of
g-tubulin reflect proteins loading. (Upper panel) Temporal expression pattern of X-PAK5 during early development (from stage 5 to stage 24). (Bottom panel)
Temporal expression pattern of X-PAK5 from blastula to gastrula. Level of X-PAK5 increases during the course of gastrulation when zygotic expression starts
and levels remain constant from stage 10 until at least stage 24. In control, temporal expression of X-PAK2 is shown. Note that X-PAK2 antibodies reveala
doublet in embryonic lysates and the signal associated with the bottom band increases during the course of development. The same pattern is observed during
early development if antibodies directed against the C-terminal region of X-PAK2 are used for Western blot detection suggesting that the bottom band is not a
proteolytic product of X-PAK2. This lower band is not detected in Xenopus oocytes (Cau et al., 2000). However, it is repeatedly detected around stage 9 during
development and is likely due to either a posttranslational modification of X-PAK2 or to the expression of a zygotic closely related X-PAK2 isoform whose
expression increases after MBT. MBT, midblastula transition. (B) Spatial distribution of X-PAK5 across the animalegetal axis. Xenopus embryos were
dissected at stage 10+
into animal poles (A), equatorial marginal zones (M), and vegetal regions (V). Control whole embryos (We) were harvested at the same
stage and embryonic lysates performed. Since cell size varies greatly across the animalegetal axis, protein extracts were standardized byWestern blot analysis
using h-tubulin as a loading control for cellular volume. Western blot analyses of similar volumes of dissected pieces and whole embryos (with respect to the
h-tubulin control) are shown. X-PAK5 protein is mainly localized in the animal pole and the equatorial marginal zone in the early gastrula embryo. (C)
Immunostaining of X-PAK5 across the dorsoventral axis. Xenopus embryos were fixed in MEMFA at the onset of gastrula (stage 10+), at midgastrula (stage
10.25), and late gastrula (stage 11.5), and bisected along the dorsoventral axis for immunohistochemistry. Dorsoventral orientation was determined by the dorsal
blastopore lip. X-PAK5 expression is essentially located in the ectoderm and in marginal zone cells including the mesodermal-fated cells that migrate inwards the
embryo. Some staining was also detected in nuclei of endodermal cells. No significant signal was detected in immunohistochemical control detection when
primary antibody addition was omitted. (D) Subcellular localization of endogenous X-PAK5 in animal explants (dissected at stage 8) and dorsal marginal zone
(DMZ) explants (dissected at stage 10.25) using anti-PAK5 Abn122. Immunodetection of g-catenin on cap explants serves as a control for cellell junction
staining. Abbreviations: mdm, migrating dorsal mesoderm; dbl, dorsal blastopore lip; ivm, involuting ventral mesoderm; idm, involuting dorsal mesoderm. Image published in: Faure S et al. (2005) Copyright © 2005. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
