XB-IMG-158556
Xenbase Image ID: 158556
|
|
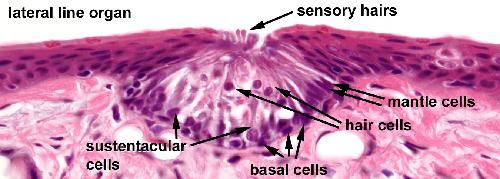
Lateral line organs of the skin. The lateral line organs are small, elongated structures on the head and trunk of Xenopus. Hair cells on the surface are called neuromasts an respond to a flow of water over the surface. Each neuromast consists of a group of cells embedded in the epidermis. The mantle cells lie peripherally and surround the centrally positioned sensory and supporting sustentacular cells. The sustentacular cells extend from the basement membrane to the outer surface. The sensory hair cells extend to the free surface, but to not reach the basement membrane. The sensory hairs of the hair cells consist of one kinocilium and 20-40 stereo cilia which are enclosed by a gelatinous cupola. The basal cells are attached to the basement membrane but do not reach the free surface.
Image from AF Wiechmann and CR Wirsig (2003) "Color Atlas of Xenopus laevis Histology", (page 88, Chapter 9, Integument: Figure 7). Copyright 2003. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Reproduced with kind permission from Springer Science & Business Media B.V. Image published in: Color Atlas of Xenopus laevis Histology Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
