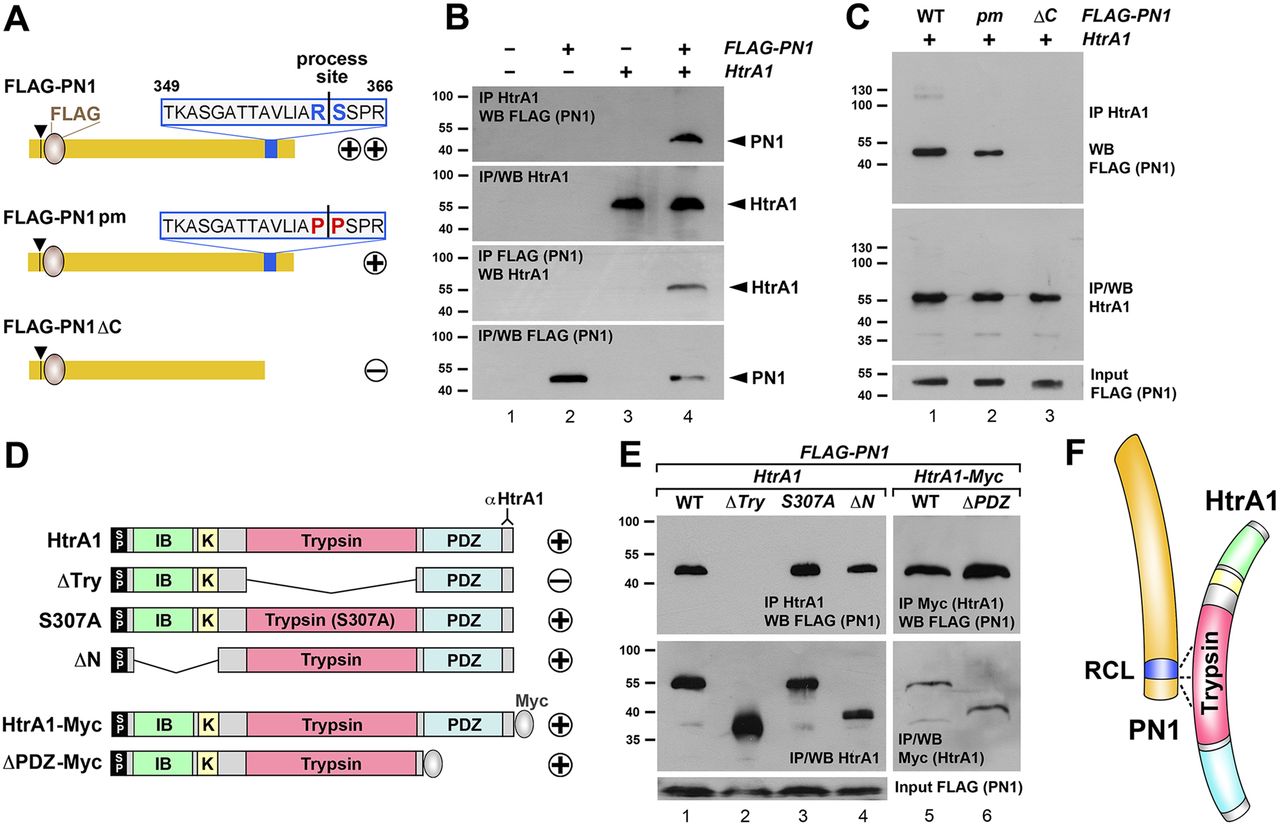
Fig. 3. PN1 binds to HtrA1. (A) Overview of FLAG-tagged protein constructs of wild-type PN1, point mutant PN1pm and C-terminal deletion mutant PN1δC. Arrowhead indicates the signal peptide cleavage site and numbers indicate the amino acid position of the reactive center loop (RCL). Plus/minus signs indicate binding to HtrA1 protein. (B) HtrA1 co-immunoprecipitates with FLAG-PN1, and FLAG-PN1 in turn co-immunoprecipitates with HtrA1 in mRNA-injected embryos at stage 17. (C) Overexpressed HtrA1 immunoprecipitates FLAG-PN1pm less efficiently than FLAG-PN1 and fails to immunoprecipitate FLAG-PN1δC in embryos at stage 10.5. (D) Overview of wild-type and mutant HtrA1 protein constructs. Plus/minus signs indicate binding to PN1 protein. SP, signal peptide; IB, IGF-binding domain; K, kazal-type serine protease inhibitor domain; Trypsin, trypsin-like serine protease domain; PDZ, PSD95/DLG1/ZO1 domain. The region recognized by HtrA1 antibody is indicated. (E) All indicated HtrA1 constructs, except HtrA1δTry, immunoprecipitate FLAG-PN1 at similar levels in embryos at stage 11. (F) Model of PN1-HtrA1 interaction. The trypsin domain of HtrA1 binds to the RCL-containing C-terminus of PN1. (B,C,E) mRNA amounts were: HtrA1-derived, 100â pg; PN1-derived, 300â pg.
Image published in: Acosta H et al. (2015)
Copyright © 2015. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher.
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-147734