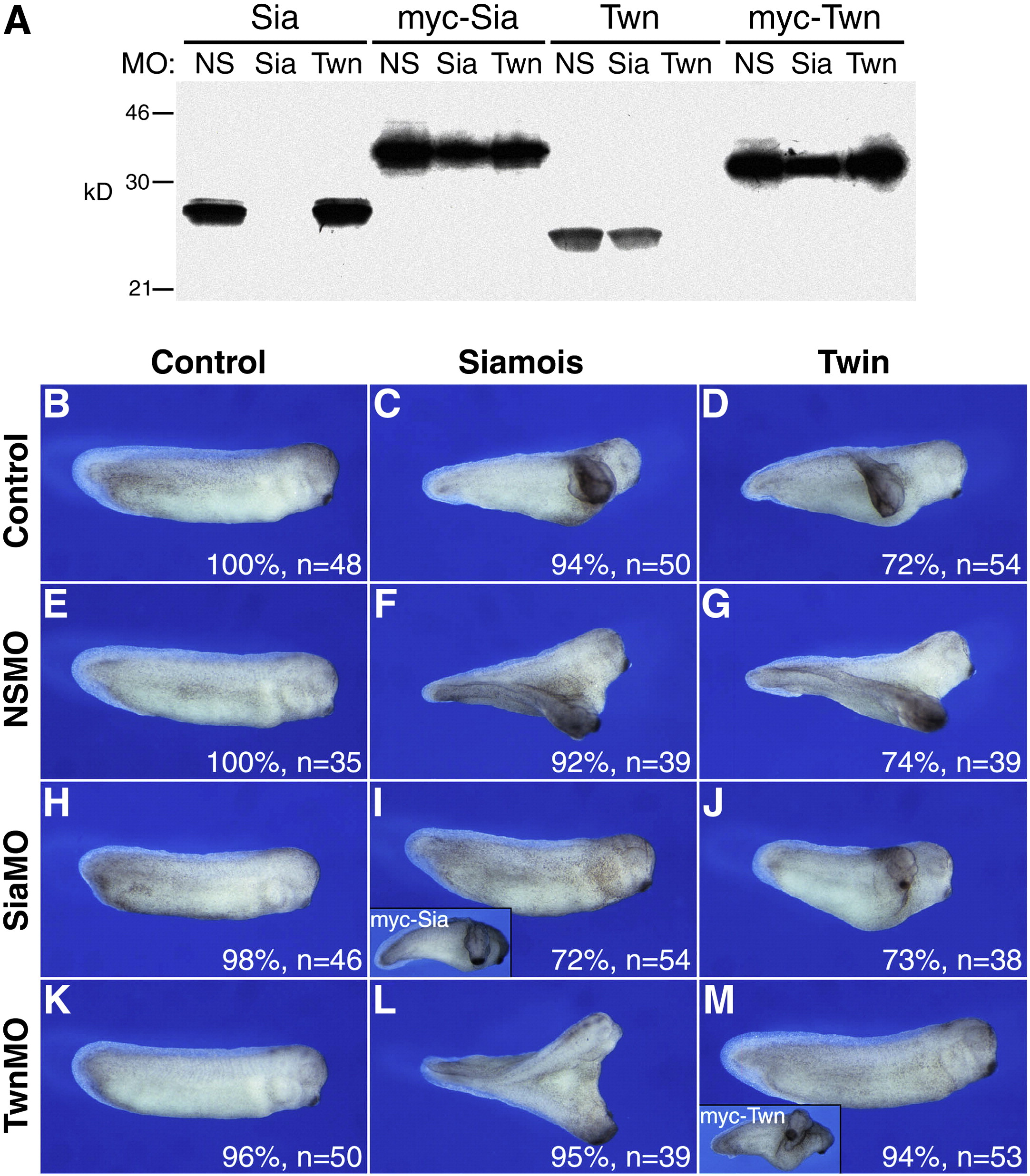
Supplementary Fig. 2. Morpholino antisense oligonucleotides specifically block the translation and biological activity of Siamois and Twin. (A) In vitro translation reactions incubated with DNA constructs (1 μg) encoding native Sia or Twn, or myc-tagged forms of Sia or Twn, in the presence of oligonucleotides (100 ng) specific for Sia or Twn, or a non-specific control oligonucleotide (NS). Translation products were labeled with 35S-methionine, resolved by 12% SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. Protein size markers are on the left. The Sia MO blocked translation of Sia, but not Twn. The Twn MO blocked translation of Twn, but not Sia. Neither oligonucleotide blocked translation of myc-Sia or myc-Twn, which have distinct upstream translation start sites. The NSMO oligonucleotide had no translation blocking activity for any of the proteins. (B–M) Inhibition of axis induction by Sia- or Twn-specific oligonucleotides. At the 4-cell stage both ventral blastomeres were injected with (E–G) a non-specific control morpholino oligonucleotide (NSMO, 25 ng), (H–J) a Sia-specific oligonucleotide (SiaMO, 25 ng), or (K–M) a Twn-specific oligonucleotide (TwnMO, 25 ng). At the 8-cell stage a single ventral blastomere was injected with 20 pg of (C,F,I,L) Sia, (D,G,J,M) Twn, (I, inset) myc-Sia, or (M, inset) myc-Twn mRNA. The Sia MO blocked axis induction by Sia (I), but not Twn (J). The Twn MO blocked axis induction by Twn (M), but not Sia (L). myc-Sia and myc-Twn were insensitive to the corresponding oligonucleotides and the NSMO oligonucleotide did not block axis induction for either Sia or Twn. Whole embryo morphology (dorsal up and anterior right) is shown at the tailbud stage, with percentage of embryos displaying the representative phenotype and total embryos analyzed indicated in the lower right for each panel. (B) Uninjected control embryo.
Image published in: Bae S et al. (2011)
Copyright © 2011. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
| Experiment + Assay | Source | Phenotypes and Disease | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xla Wt + sia1 + NF32 (morphology) | fig.S2.c |
| ||
| Xla Wt + sia2 + NF32 (morphology) | fig.S2.d |
|
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-152449