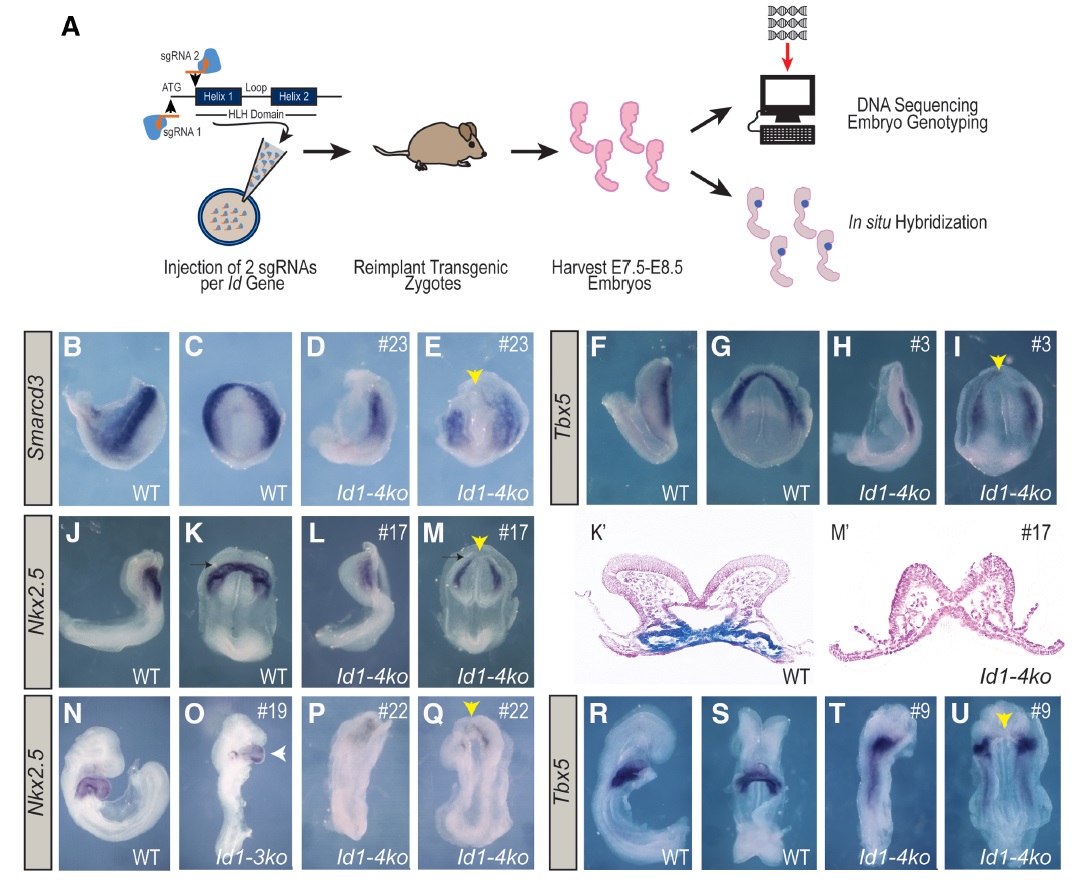
Figure 6. Id genes are essential for early heart formation. (A) Schematic illustrating the generation and analysis of Id1–4 mutant embryos using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Two sgRNAs per gene (targeting the translational start site and the HLH domain) were injected into single- cell mouse zygotes alongside Cas9 mRNA. Zygoteswere reimplanted and harvested at stages E7.5–E8.5. Resulting embryos were genotyped by DNA deep sequencing, and cardiac gene expression was assessed via whole-mount in situ hybridization. (B–U) In situ hybridization results from the most severe Id1–4 mutants—compared with wild type (individual mutants are marked by #)—plus one less-affected mutant (O); analysis of Smarcd3 at E7.75 (B–E), Tbx5 at E8.0 (F–I), Nkx2.5 at E8.25 (J–M; plus transverse sections through the heart tube-forming region [K′,M′]), Nkx2.5 at E8.5 (N–Q), and Tbx5 at E8.5 (R–U). (Yellow arrowheads) Missing heart tube (or missing heart tube-forming region at cardiac crescent stages) in Id1–4 mutants; (white arrowhead) malformed heart tube; (black arrows) the plane of transverse sectioning through the heart tube-forming region; (black dashed arrows) posterior–lateral cardiac regions. See the Supplemental Material for detailed sequencing results of mutant embryos.
Image published in: Cunningham TJ et al. (2017)
© 2017 Cunningham et al. Creative Commons Attribution license
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-173442