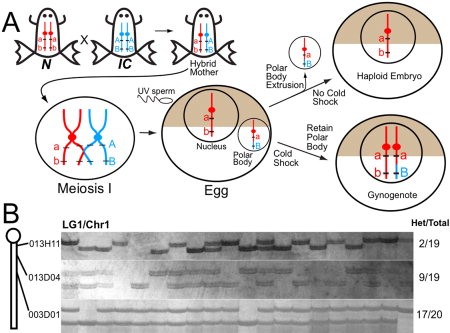
Figure 1. Gynogenesis and centromere mapping. A:X. tropicalis N and IC strains differ at many sequence polymorphisms, schematized in red and blue. Hybrids contain both N and IC parental chromosomes, which recombine during meiosis I. Shortly after fertilization, one set of sister chromatids is extruded as a polar body, resulting in a haploid embryo if eggs are fertilized with ultraviolet-irradiated sperm. Cold shock suppresses polar body formation, resulting in a gynogenote containing the sister chromatids of meiosis II. Loci very close to centromeres are homozygous in gynogenotes, but meiotic recombination can produce heterozygous noncentromeric loci. B: Centromeres were mapped by assaying frequency of homozygosity at polymorphic loci in gynogenotes. Three markers on Chr 1/LG1 were tested on the same set of gynogenotes. Proximity to centromere is reflected by relative frequency of heterozygosity, with marker 013H11 (2/19) closer than 013D04 (9/19) and 003D01 (17/20).Download figure to PowerPoint
Image published in: Khokha MK et al. (2009)
Copyright © 2009. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, John Wiley & Sons.
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-83616