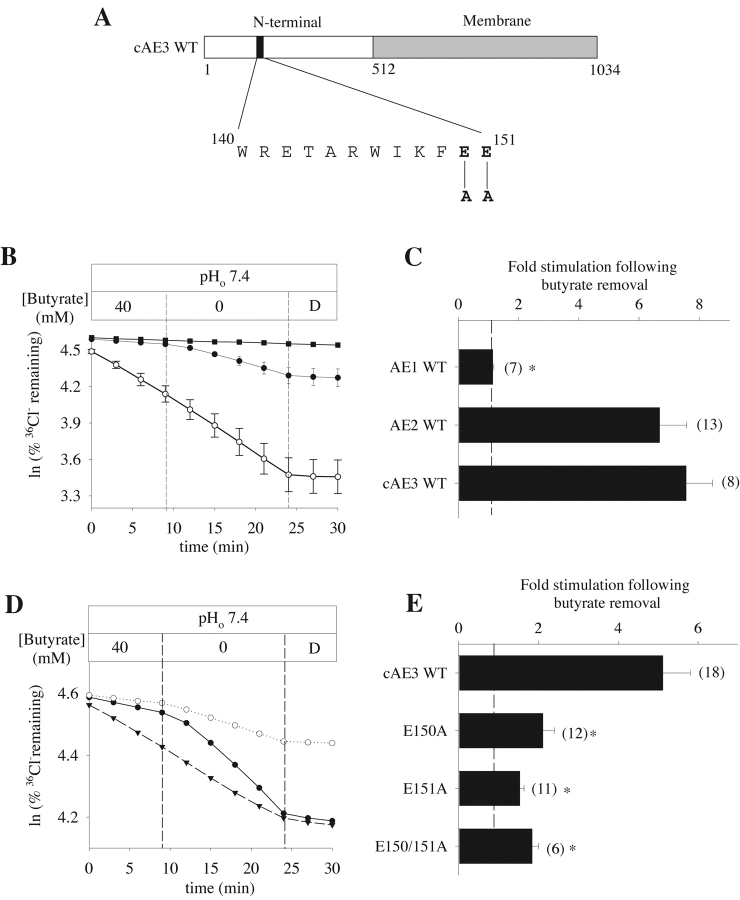
Figure 8. . Mutation of corresponding glutamate residues in the cAE3 NH2-terminal cytoplasmic domain similarly alters regulation by pHi. (A) Schematic showing site of alanine substitutions for conserved glutamate residues in the NH2-terminal cytoplasmic domain of rat cAE3. (Rat cAE3 residues E150 and E151 correspond to rat bAE3 residues E347 and E348.) (B) Representative 36Cl− efflux time course from oocytes previously injected with water (filled squares), with cRNA encoding mouse kidney AE1 (open circles), or rat cAE3 (filled circles) during removal of butyrate and subsequent inhibition with DIDS (D, 200 μM). (C) Mean fold stimulation of 36Cl− efflux by intracellular alkalinization (butyrate removal) in oocytes expressing either AE1, AE2, or cAE3. (D) Representative 36Cl− efflux time course from oocytes expressing wild-type cAE3 (filled circles) or the cAE3 mutants E150A (open circles) or E151A (closed triangles) during butyrate removal and subsequent inhibition by DIDS (D, 200 μM). (E) Mean fold stimulation of 36Cl− efflux by intracellular alkalinization (butyrate removal) in oocytes expressing either wild-type cAE3, the cAE3 mutants E150A or E151A, or the double mutant E150A/E151A. Values in C and E are means ± SEM for n oocytes; dashed lines at onefold indicate no stimulation by butyrate removal. Asterisk indicates P < 0.05.
Image published in: Stewart AK et al. (2002)
Copyright © 2002, The Rockefeller University Press. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-121217