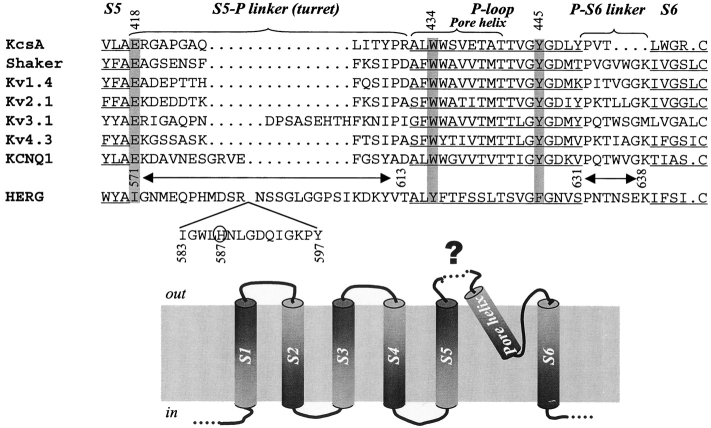
Figure 1. . (Top) Alignment of amino acid sequences from the end of S5 to the beginning of S6 of HERG, major classes of voltage-gated K (Kv) channels, and KcsA. Transmembrane and pore (P)-loop regions are underlined. S5 and S6 correspond to M1 and M2 of KcsA, respectively. S5-P linker (“turret” of KcsA) and P-S6 linker (P-M2 of KcsA) are marked. Gaps (…) are introduced to improve alignment. Amino acids in the Shaker channel implicated in hydrogen bonding and critical for maintaining the outer mouth in the open state are highlighted by gray shade: E418, W434, and Y445 (Shaker position numbers shown on top). Note that these amino acids are conserved in KcsA and all major classes of Kv channels, but not in HERG. The HERG positions examined here (571–613 of S5-P linker, and 631–638 of P-S6 linker) are marked above its sequence. Positions 583–597 are shown as an insert. H587 in HERG is circled (see text for discussion). (Bottom) Transmembrane topology of one Kv channel subunit. The structure of the unusually long extracellular S5-P linker of HERG (marked by a dotted line and “?”) is the major focus of this study.
Image published in: Liu J et al. (2002)
Copyright © 2002, The Rockefeller University Press. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-121262