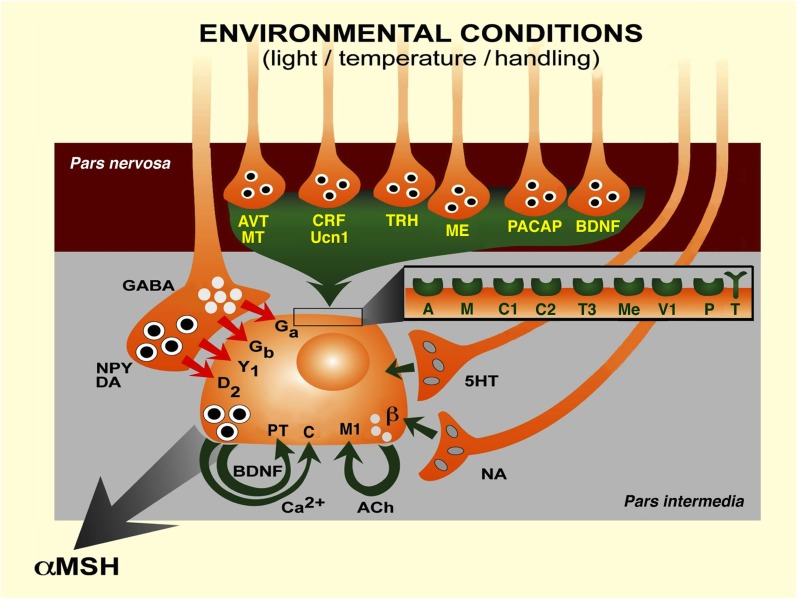
Figure 2. Transduction of various physiological environmental stimuli to the melanotrope cell of Xenopus laevis controlling the secretion of αMSH, via neurohemal nerve terminals in the pars nervosa and from synaptic terminals in the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland. 5HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin); A, arginine-vasopressin receptor; ACh, acetylcholine; AVT, arginine-vasopressin; β, β-adrenergic receptor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; C, calcium-sensing receptor; C1, corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1; C2, corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 2; Ca2+, calcium ion; CRF, corticotropin-releasing factor; D2, dopamine D2 receptor; DA, dopamine; Ga, GABAA receptor; Gb, GABAB receptor; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; M, mesotocin receptor; M1, muscarinic M1 receptor; ME, metenkephalin; Me, metenkephalin receptor; MT, mesotocin; NA, noradrenalin; NPY, neuropeptide Y; P, P75NTR receptor; PACAP, pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide; T, TrkB receptor; T3, thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor 3; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone; Ucn1, urocortin 1; V1, VPAC1 receptor; Y1, NPY Y1 receptor. (Modified after Roubos et al., 2005.)
Image published in: Roubos EW et al. (2010)
Image downloaded from an Open Access article in PubMed Central. Copyright © 2010 Roubos, Jenks, Xu, Kuribara, Scheenen and Kozicz.
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-127178