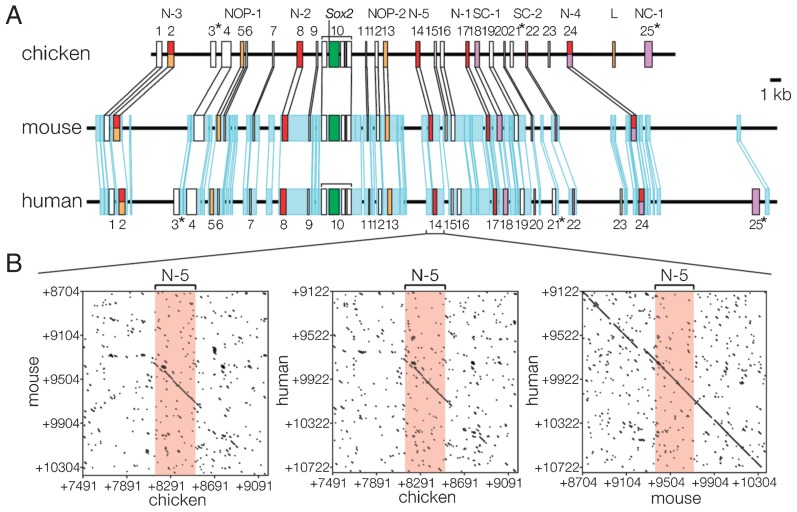
Fig. 4. Correspondence of the functionally defined Sox2 enhancers with blocks of highly conserved sequences found by comparison of chicken and mammalian Sox2 locus sequences. (A) Conserved sequence blocks found in the Sox2 locus sequences of amniotes. Blocks of sequences that show > 60% identity over the stretch of 100 base pairs are indicated by boxes. The 25 sequence blocks No. 1 to No. 25 conserved between chicken and mammalian sequences are indicated on the top. Blocks No. 3, 21 and 25 marked by asterisks are not conserved in the mouse sequence. Sequences conserved between human and mouse genomic sequences but not strongly conserved in the chicken sequence are indicated in blue. (B) Dot matrices comparing DNA sequences of the three animal sequences encompassing enhancer N-5 (conserved sequence block No. 14). A dot indicates a 10 bp sequence with > 60% matching. Between the chicken and mammalian sequences, only the enhancer sequence is significantly conserved, however between human and mouse, the enhancer sequence is embedded in a broader region of possibly non-functional sequence conservation. Adapted from Fig. 6 in Uchikawa et al. (2003). Functional analysis of chicken Sox2 enhancers highlights an array of diversity regulatory elements that are conserved in mammals. Dev. Cell 4, 509–519, with permission from Elsevier.
Image published in: Kamachi Y et al. (2009)
Image downloaded from an Open Access article in PubMed Central. © 2009 The Japan Academy
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-128040