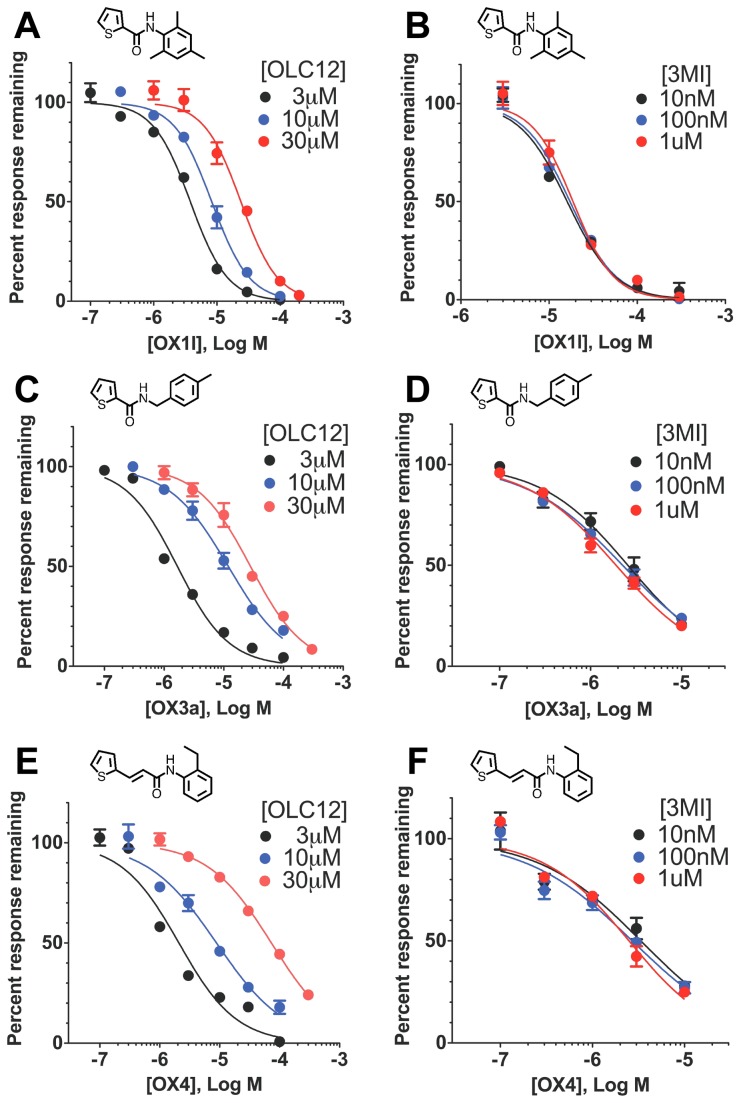
Figure 5. The potent Orco antagonists OX1l, OX3a and OX4 non-competitively inhibit odorant activation of a mosquito OR.A. Altering the concentration of Orco agonist (OLC12) shifts the OX1l inhibition curve. The IC50 for OX1l inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 10 µM OLC12 (8.3 ± 0.5 µM, n = 4) is significantly different from the IC50 for OX1l inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 3 µM OLC12 (3.8 ± 0.3 µM, n = 9) (p<0.0001, F-test). The IC50 for OX1l inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 30 µM OLC12 (24 ± 3 µM, n = 6) is significantly different from the IC50 for OX1l inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 3 µM OLC12 (p<0.0001, F-test) and from the IC50 for OX1l inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 10 µM OLC12 (p<0.0001, F-test). B. Altering odorant (3MI) concentration fails to alter the inhibition curve for OX1l antagonism of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activated by 3MI. The IC50 values for OX1l inhibition of responses to 10 nM 3MI (17 ± 1 µM, n = 3), 100 nM 3MI (16 ± 1 µM, n = 3), and 1µM 3MI (19 ± 2 µM, n = 3) did not differ (p=0.3605, F-test). C. Altering the concentration of Orco agonist (OLC12) shifts the OX3a inhibition curve. The IC50 for OX3a inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 10 µM OLC12 (12 ± 1 µM, n = 3) is significantly different from the IC50 for OX3a inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 3 µM OLC12 (1.7 ± 0.2 µM, n = 4) (p<0.0001, F-test). The IC50 for OX3a inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 30 µM OLC12 (28 ± 2 µM, n = 3) is significantly different from the IC50 for OX3a inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 3 µM OLC12 (p<0.0001, F-test) and from the IC50 for OX3a inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 10 µM OLC12 (p<0.0001, F-test). D. Altering odorant (3MI) concentration fails to alter the inhibition curve for OX3a antagonism of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activated by 3MI. The IC50 values for OX3a inhibition of responses to 10 nM 3MI (2.6 ± 0.3 µM, n = 3), 100 nM 3MI (2.3 ± 0.2 µM, n = 4), and 1µM 3MI (1.9 ± 0.1 µM, n = 3) did not differ (p=0.07, F-test). E. Altering the concentration of Orco agonist (OLC12) shifts the OX4 inhibition curve. The IC50 for OX4 inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 10 µM OLC12 (8.8 ± 1.2 µM, n = 3) is significantly different from the IC50 for OX4 inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 3 µM OLC12 (2.1 ± 0.3 µM, n = 5) (p<0.0001, F-test). The IC50 for OX4 inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 30 µM OLC12 (73 ± 5 µM, n = 3) is significantly different from the IC50 for OX4 inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 3 µM OLC12 (p<0.0001, F-test) and from the IC50 for OX4 inhibition of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activation by 10 µM OLC12 (p<0.0001, F-test). F. Altering odorant (3MI) concentration fails to alter the inhibition curve for OX4 antagonism of Cqui\Orco+Cqui\Or21 activated by 3MI. The IC50 values for OX4 inhibition of responses to 10 nM 3MI (3.4 ± 0.6 µM, n = 3), 100 nM 3MI (2.7 ± 0.4 µM, n = 3), and 1µM 3MI (2.5 ± 0.3 µM, n = 3) did not differ (p=0.42, F-test).
Image published in: Chen S and Luetje CW (2013)
Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. Creative Commons Attribution license
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-129449