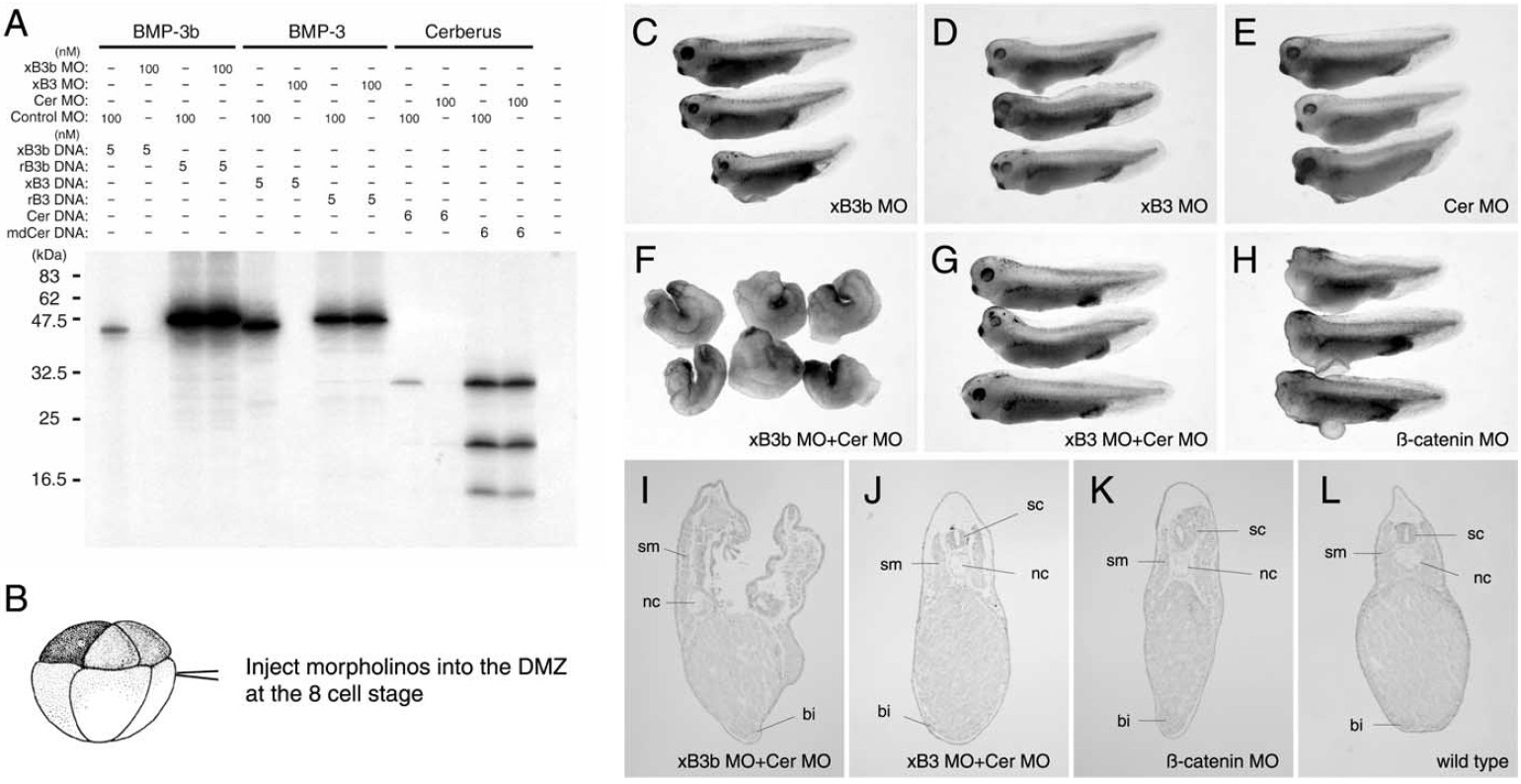
Fig. 8. Inhibition of both xBMP-3b and cerberus causes headless embryos. (A) Specificity of morpholino antisense oligonucleotides (MO) of xBMP-3b, xBMP-3 and cerberus. Translation of mRNAs encoding Xenopus proteins is inhibited, but neither rat BMP-3b/3 nor mdCerberus are affected by MOs. Target sequences for cerberus MO are altered in mdCerberus mutant, but not the amino acid sequences. Messenger RNAs and proteins were prepared from plasmid DNAs as described in Materials and methods. (B) Schematic diagram of embryonic stage and injection point of MOs. (CâE) Independent injections of xBMP-3b, xBMP-3, and cerberus MOs (10 ng) did not perturb Xenopus embryos. (F, G) Simultaneous injection of xBMP-3b and cerberus MOs (5 ng each) led to headlessness (54%, n 22), whereas that of xBMP-3 and cerberus MOs did not (0%, n 21). (H) Injection of -catenin MO (10 ng) caused headless embryos (92%, n 25). (IâL) Histological sections of embryos injected with xBMP-3b and cerberus MOs (F), xBMP-3 and cerberus MOs (G), -catenin MO (H), and wild type. sm, somite; nc, notochord; sc, spinal cord; bi, blood island.
Image published in: Hino J et al. (2003)
Copyright © 2003. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-130820