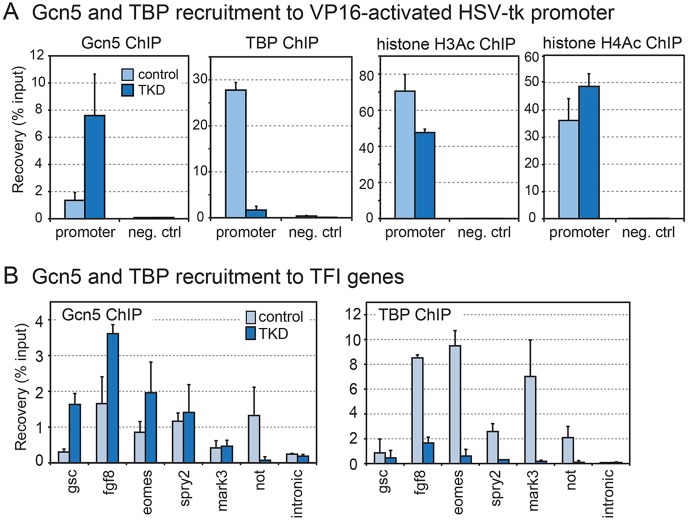
Fig. 5. Increased promoter binding of Gcn5 in TBP family triple-knockdown embryos. (A) ChIP analysis of Gcn5, TBP and histone H3 and H4 acetylation under VP16 activating conditions in TKD and control embryos. These experiments were performed in a VP16 transcription activation assay combined with TBP family loss-of-function experiments (cf. Fig. S3). Loss of TBP on the promoter in TKD embryos is compensated by an increase in Gcn5 (first two panels). Histones H3 and H4 are acetylated in both TKD and control embryos (second two panels). (B) Gcn5 is recruited to TFI gene promoters in TBP family triple-knockdown embryos. ChIP reveals enhanced Gcn5 binding when TBP and TBP-related factors are depleted in TKD embryos (blue) compared with water-injected controls (light blue). The intronic region of nadh gene shows background levels. The mark3 gene requires normal TBP levels for expression.
Image published in: Gazdag E et al. (2016)
© 2016. Creative Commons Attribution license
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-151531