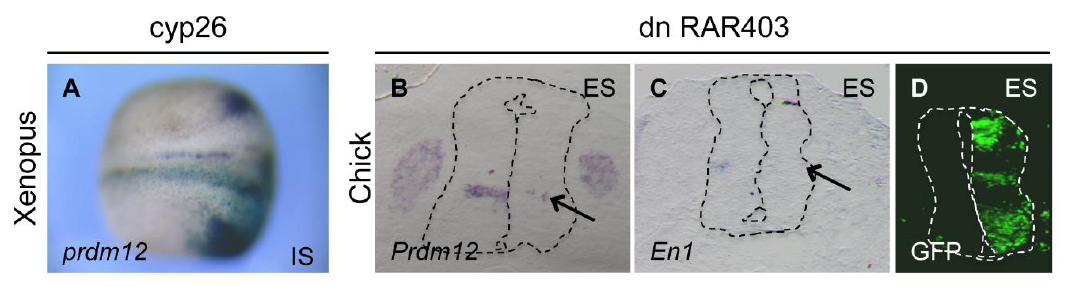
Fig. S6. Inhibition of retinoic acid signaling reduces Prdm12 expression. (A) Dorsal view of a Xenopus neurula stage embryo injecled with cyp26 mRNA (500 pg/blastomere) and hybridized for prdm12. LacZ mRNA was used as a lineage tracer (light blue). IS, injected side. (6, C) In situ hybridization revealing Prdm12 and En1 expression (as V1 markers) on transverse sections of the neural tube of HH24 chick embryos. with the right side overexpressing a dominant negative form of the human retinoic acid receptor a (dnRAR403). (D) Control immunofluorescence with GFP antibodies to reveal the transfected side. Note the reduction of prdm12 in the Xenopus neural plate of Cyp26 mRNA injected embryos (58% affected, n=120) and the decrease of both Prdm12 and En1 staining (arrows) in the chick neural tube. ES: electroporation side.
Image published in: Thélie A et al. (2015)
Copyright © 2015. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| prdm12.L | LOC108699953, pfm9 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 | posterior placodal area neural plate |
Image source: Published
| Experiment + Assay | Source | Phenotypes and Disease | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xla Wt + cyp26a1 + NF13 (in situ hybridization) | Fig. S6.a |
|
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-151843