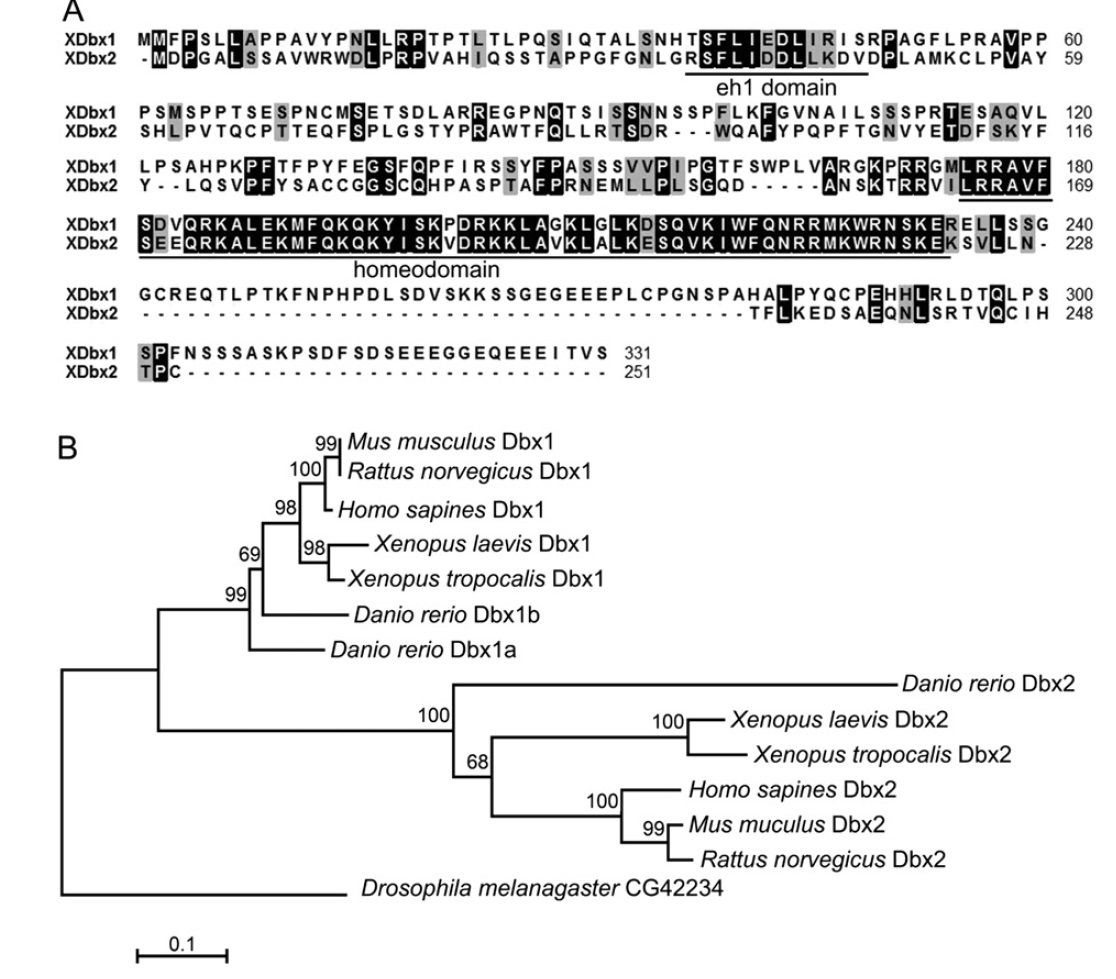
Fig. 1. Alignment and phylogenetic analysis of X. laevis Dbx proteins. (A) Alignment of the XDbx1 and XDbx2 protein sequences. Identical amino acids are high-lighted by black background. The conserved eh1 domain and homeodomain are underlined. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of human, rat, mouse, X. tropicals and laevis, zebrafish and Drosophila Dbx family proteins. ClustalW alignment, Poisson correction model, and Bootstrap test (500 replicates) were used for the neighbor-joining (NJ) tree construction. The accession number of the proteins used are Mus musculus Dbx1, Ensembl protein ID: ENSMUSP00000032717; Mus musculus Dbx2, Ensembl protein ID: ENSMUSP00000060424; Rattus norvegicus Dbx1, Ensembl protein ID: ENSRNOP00000019739; Rattus norvegicus Dbx2, Ensembl protein ID: ENSRNOP00000009143; Homo sapines Dbx1, Ensembl ID: ENSP00000227256; Homo sapines Dbx2, Ensembl protein ID: ENSP00000331470; Danio rerio Dbx1a, NP_571233; Danio rerio Dbx1b, Ensembl protein ID: ENSDARP00000013350; Danio rerio Dbx2, Ensembl protein ID: ENSDARP00000057729; Xenopus tropocalis Dbx1, XP_002940015; Xenopus tropocalis Dbx2, XP_002932867; Xenopus leavis Dbx1, NP_001079210.
Image published in: Ma P et al. (2011)
Copyright © 2011. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-154321