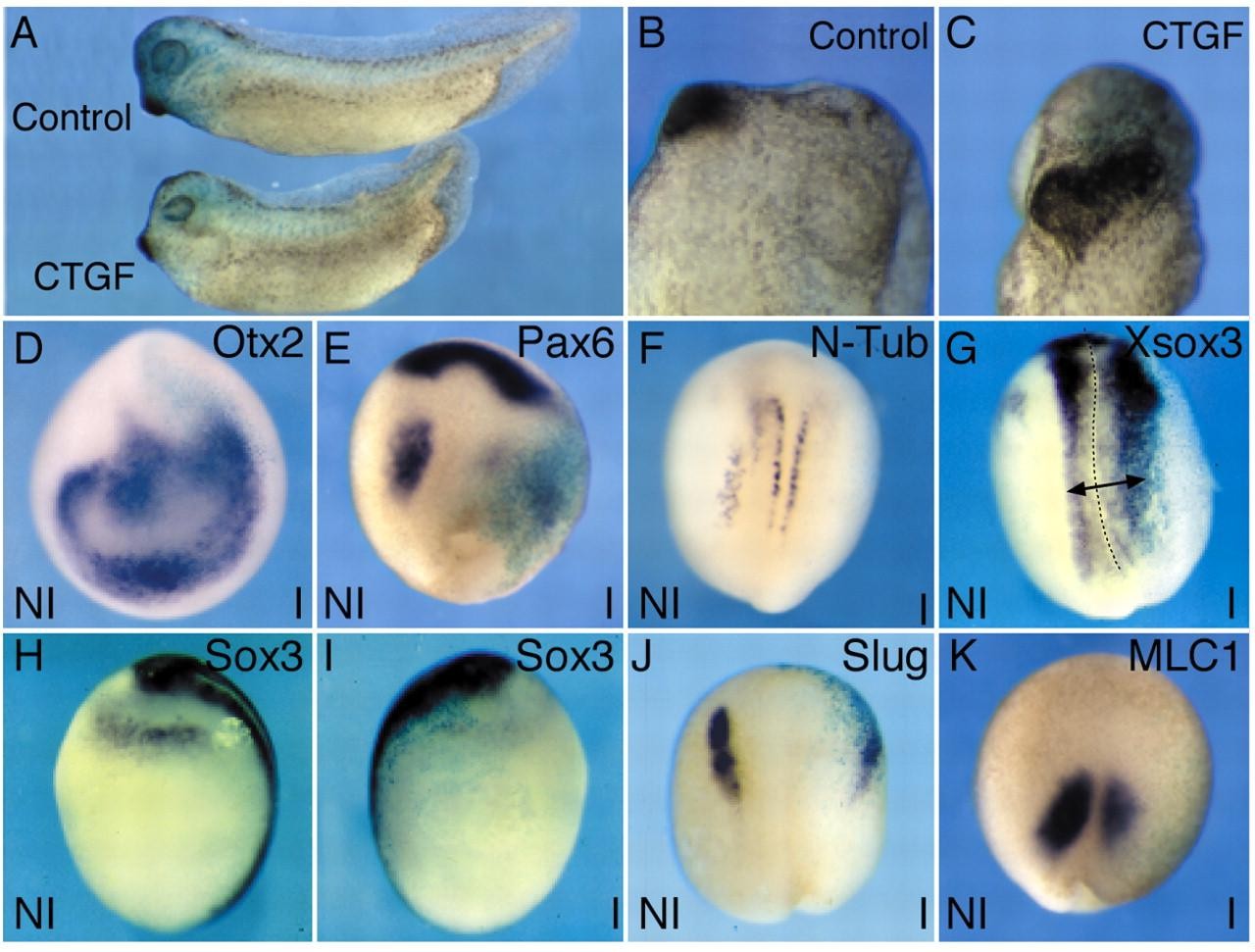
Fig. 2. The effects of overexpression of CTGF resemble those caused by inhibition of WNT signalling. (A) Overexpression of CTGF (bottom embryo) causes a shortening of Xenopus embryos. Three independent experiments were performed with similar results each time. (B,C) Compared with controls (B), CTGF-injected embryos have an enlarged cement gland (C). (D-K) Unilateral overexpression of CTGF causes changes in gene expression that resemble those caused by inhibition of WNT signalling. (D) The expression domain of Otx2 is expanded. (E) CTGF causes a down-regulation of the future hindbrain domain of Pax6 and slightly expands the anterior domain. (F) CTGF causes down-regulation of N-tubulin in the neural plate. (G) The expression domain of Xsox3 in the neural plate is expanded. (H,I) Compared with the control side of the embryo (H), CTGF causes down-regulation of XSox3 in the dorsolateral placode (I). (J) CTGF causes down-regulation of Slug. (K) The muscle-specific gene myosin light chain 1 (MLC1) is down-regulated by Ctgf. I: injected; NI: Not injected. The injected sides of embryos are identified by pale blue lacZ staining.
Image published in: Mercurio S et al. (2004)
Copyright © 2004. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pax6.L | an2, mgda, pax-6, pax6-a, pax6-b, wagr, XLPAX6, xpax6 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 to NF stage 21 | neural tube |
| sox3.S | Sry, Xlsox3, xSox3, Xtsox3 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 to NF stage 21 | neural plate |
| snai2.L | slug, snai2-a, snai2-b, Snail2, xSlu, xslug, XSnail2 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 to NF stage 21 | neural crest |
| mlc1.L | LOC108711162, lvm, mlc, mlc1-3 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 to NF stage 21 | somite |
| otx2.S | otx-2, otx2-a, otx2-b, otxA, Xotx-2, Xotx2 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 18 | neuroectoderm anterior neural fold pre-chordal neural plate |
| tubb2b.S | NBT, neural beta-tubulin, NST, N-Tub, n-tubulin, ntubulin, Xn-tubulin | X. laevis | Sometime during NF stage 18 to NF stage 19 | neural plate Rohon-Beard neuron neuroectoderm |
Image source: Published
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-24699