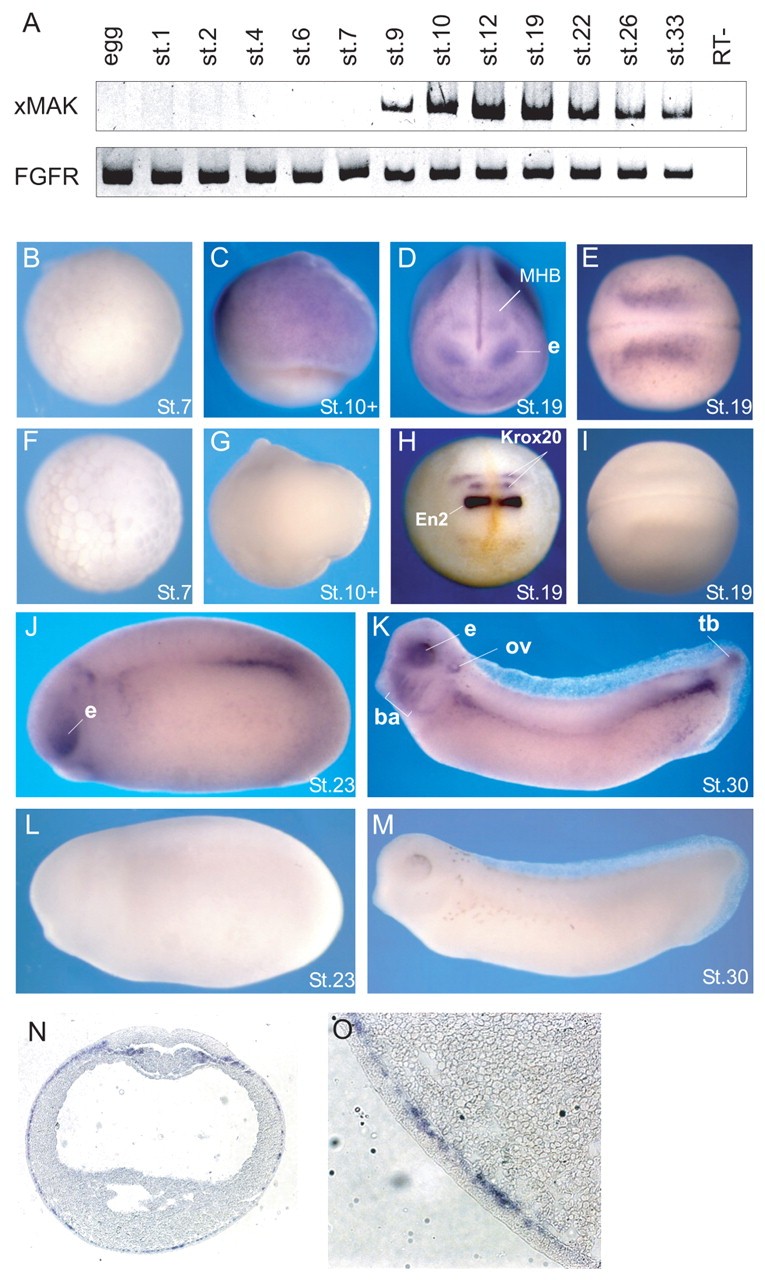
Fig. 1. xMAK expression is dynamically regulated during Xenopus development. (A) The analysis of xMAK expression at different developmental stages. Total RNA from embryos isolated at different developmental stages was used for RT-PCR. FGFR served as a loading control. RT-, no reverse transcriptase. (B-M) Spatial distribution of xMAK RNA revealed by whole-mount in situ hybridization of albino embryos at indicated stages. (B-E,J,K) xMAK antisense probe. (F,G,I,L,M) xMAK sense probe. (D) Anterior view; e, eye; MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary. (H) En2 and Krox20 probes, anterior view. En2 is expressed as a bright band at the MHB, located anterior to Krox20, which marks rhombomeres 3 and 5. (B,F) Animal pole view; (C,G) lateral view; (E,I) dorsal view, anterior is towards the left. (J-M) Lateral view, anterior is towards the left. (K) e, eye; ov, otic vesicle; ba, branchial arches; tb, tailbud. (N,O) A cross-section of a stage 17 neurula embryo after in situ hybridization with xMAK antisense probe. Staining is observed in the deep (sensorial) layer of epidermal ectoderm (magnified view shown in O) and in somitogenic mesoderm.
Image published in: Kibardin A et al. (2006)
Copyright © 2006. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nuak1.L | ark5, metastasis associated kinase, SNF1-related protein kinase, sucrose non fermenting 1-related protein kinase | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 10 | ectoderm involuted dorsal mesoderm involuted ventral mesoderm |
| nuak1.L | ark5, metastasis associated kinase, SNF1-related protein kinase, sucrose non fermenting 1-related protein kinase | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 to NF stage 21 | sensorial layer of neurectoderm epidermis ectoderm mesoderm eye neural tube |
| en2.L | En-2, en2-a, en2-b, eng2, engrailed 2, engrailed-2, engrailed homolog 2, maben, xen2 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 19 | midbrain-hindbrain boundary |
| egr2.L | EGR-2, Krox-20, krox20, XKr20, XKrox-20 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 19 | neural tube |
| nuak1.L | ark5, metastasis associated kinase, SNF1-related protein kinase, sucrose non fermenting 1-related protein kinase | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 23 | midbrain-hindbrain boundary eye presomitic mesoderm tail bud |
| nuak1.L | ark5, metastasis associated kinase, SNF1-related protein kinase, sucrose non fermenting 1-related protein kinase | X. laevis | Sometime during NF stage 29 and 30 | eye branchial arch otic vesicle tail bud midbrain-hindbrain boundary presomitic mesoderm pharyngeal arch mandibular arch hyoid arch tail tip pronephric mesenchyme |
Image source: Published
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-43741