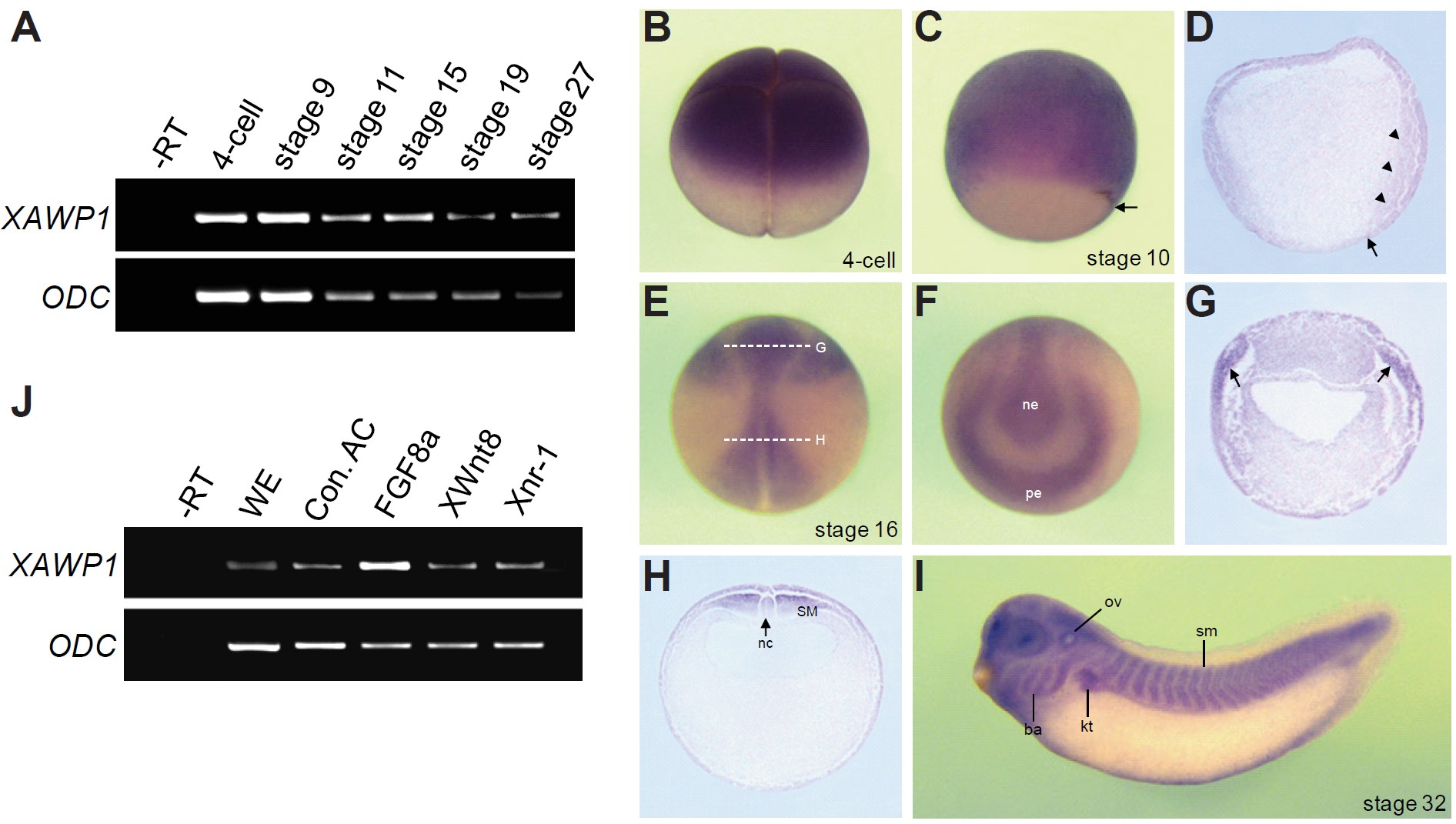
Fig. 1. Expression of the XAWP1 gene. (A) RT-PCR analysis showing the temporal expression pattern of AWP1 in Xenopus early development. Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) serves as a loading control. âRT, a stage 27 control embryo in the absence of reverse transcriptase. (B-I) Spatial expression pattern of XAWP1. (B) Animallateral view with the vegetal pole to the bottom. (C) Vegetal-lateral view with dorsal to the right. (D) Sagittal section of a stage 10.5 gastrulae. Arrows in (C,D) denote the dorsal blastopore lip. Arrowheads indicate the involuting dorsal mesoderm. (E) Dorsal view with anterior to the top. (F) Anterior view of the embryo shown in (E) with dorsal to the top. ne, neural ectoderm; pe, preplacodal ectoderm. (G,H) Transverse sections of the embryo in (E) at the levels indicated by the dashed lines. Arrows in (G) denote the preplacodal ectoderm. SM, somitic mesoderm; nc, notochord; ov, otic vesicle; ba, branchial arch; kt, kidney tubule; sm, somites. (J) Four-cell stage embryos were injected in the animal pole region as indicated with FGF8a (1 ng), XWnt8 (400 pg) and Xnr-1 (100 pg) and then animal caps were excised at stage 9 and cultured to stage 10.5 for RT-PCR analysis. WE, a stage 10.5 whole embryo. Con. AC, uninjected control animal caps.
Image published in: Seo JH et al. (2013)
Copyright © 2013. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, University of the Basque Country Press.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| zfand6.S | awp1 | X. laevis | Sometime during NF stage 10 to NF stage 10.5 | animal hemisphere involuting marginal zone dorsal mesoderm |
| zfand6.S | awp1 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 18 | preplacodal ectoderm paraxial mesoderm notochord |
| zfand6.S | awp1 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 32 | pharyngeal arch mandibular arch hyoid arch branchial arch somite epaxial muscle pronephric kidney otic vesicle lens placode pronephric tubule brain forebrain midbrain hindbrain |
| zfand6.S | awp1 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 3 (4-cell) | animal pole animal animal blastomere |
Image source: Published
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-86764