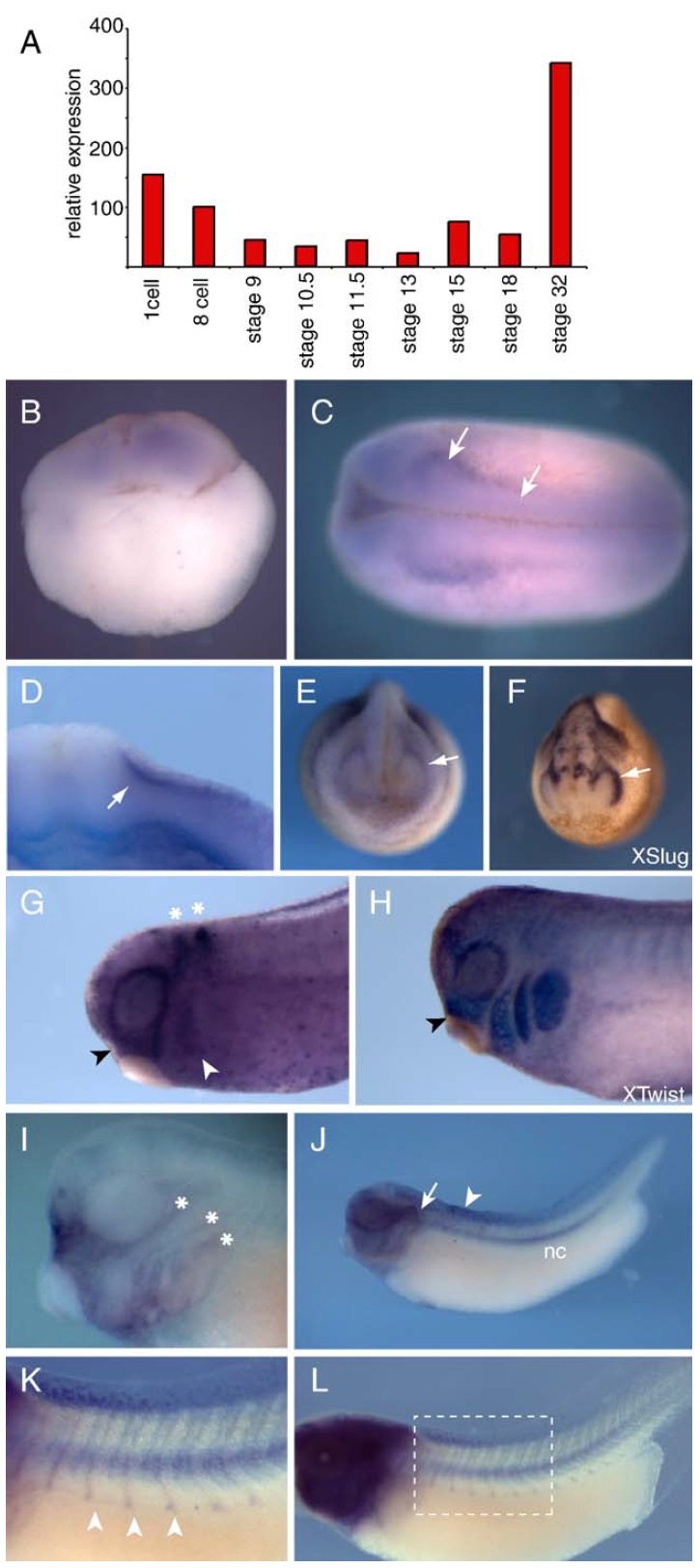
Fig. 2. Expression of Xtes during early Xenopus development. (A) Real-time RTPCR based expression profile of Xtes from stage 1 through to tail bud stage 32. Values have been normalized to those of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). (BâL) In situ hybridization analysis of Xtes expression. (B) 4-cell stage embryo. (C) Stage 18; arrows point to strong expression of Xtes next to the neural folds. (D) Cross-section at neurula stage showing Xtes expression between the epithelium and mesoderm. (EâH) Xtes expression is found in an anterior stream of cranial neural crest. (E) White arrow marks the stream of Xtes expressing cells, whose pattern is similar to the most rostral stream of XSlug positive neural crest cells (F; white arrow). (G) Xtes expression ventral to the eye (black arrowhead) corresponds to the most anterior cranial neural crest that is positive for Xtwist expression (black arrowhead in panel H). White arrowhead and asterisks in panel G denote Xkrox20 expression in rhombomeres 3 and 5 and the anterior branchial crest, respectively. (I) Expression of Xtes in the head, in an embryo in which BM purple stain development was stopped early; asterisks mark the three lateral line placodes. (J) View of a whole tail bud embryo showing strong expression in the notochord (nc). Staining was also evident in the otic vesicle (arrow) and the rostral region of the dorsal fin (arrowhead). (K, L) If the BM purple stain is allowed to develop longer, Xtes expression becomes evident along the somitic boundaries (white arrowheads in the higher magnification view in panel K).
Image published in: Dingwell KS and Smith JC (2006)
Copyright © 2006. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tes.L | tess, tess-2, xtes | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 18 | neural crest cranial neural crest |
| snai2.L | slug, snai2-a, snai2-b, Snail2, xSlu, xslug, XSnail2 | X. laevis | Sometime during NF stage 19 to NF stage 21 | mandibular crest hyoid crest branchial crest cranial neural crest |
| twist1.L | twist, twist1-a, twist1-b, X-twi, Xtwi, Xtwist | X. laevis | Sometime during NF stage 19 to NF stage 26 | cranial neural crest branchial crest hyoid crest mandibular crest |
| tes.L | tess, tess-2, xtes | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 19 to NF stage 26 | cranial neural crest |
| egr2.L | EGR-2, Krox-20, krox20, XKr20, XKrox-20 | X. laevis | Sometime during NF stage 22 to NF stage 26 | rhombomere R3 rhombomere R5 anterior branchial crest |
| tes.L | tess, tess-2, xtes | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 22 to NF stage 44 | lateral line placode notochord otic vesicle dorsal fin intersomitic region |
| tes.L | tess, tess-2, xtes | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 3 (4-cell) | animal hemisphere |
Image source: Published
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-135129