XB-IMG-119043
Xenbase Image ID: 119043
|
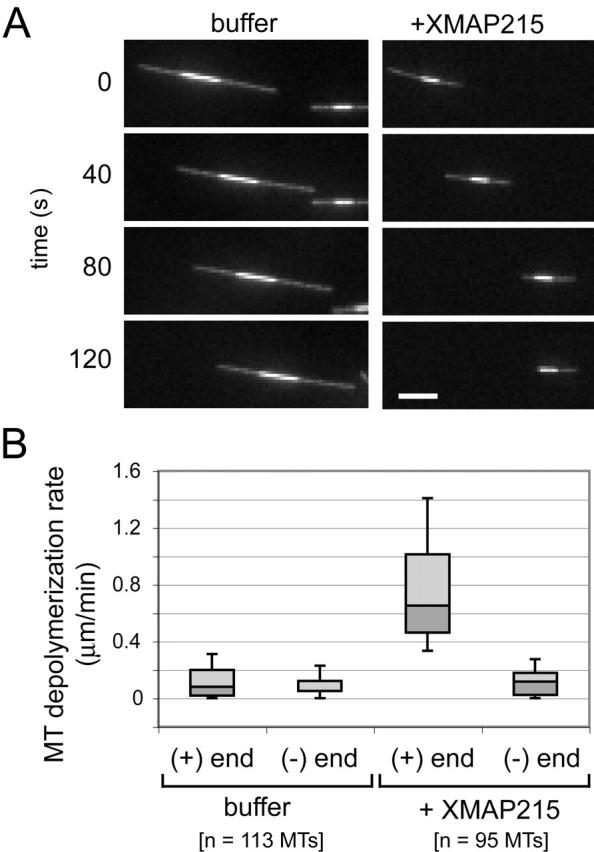
Figure 5. XMAP215 promotes CPP MT depolymerization at MT plus ends. (A) XMAP215 promotes end-dependent CPP MT depolymerization. Shown here are images from a time-lapse series of dim-bright CPP MTs (see Materials and methods) treated with buffer alone or buffer plus 19 nM XMAP215 (interval between still images is 40 s). In each sample, kinesin motility was used to determine MT polarity; translocation of the MT from left to right represents minus end leading and plus end lagging. In the XMAP215-treated sample, the plus end shortens while the minus end remains stable (see Video 1, available at http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200211095/DC1). (B) Depolymerization by XMAP215 is specific to MT plus ends. Depolymerization rates were quantitated for each MT end from experiments as in A. Error bars denote 10th and 90th percentile; 75th, 50th, and 25th percentiles are represented by the top, middle, and bottom of each box. Image published in: Shirasu-Hiza M et al. (2003) Copyright © 2003, The Rockefeller University Press. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
