XB-IMG-117508
Xenbase Image ID: 117508
|
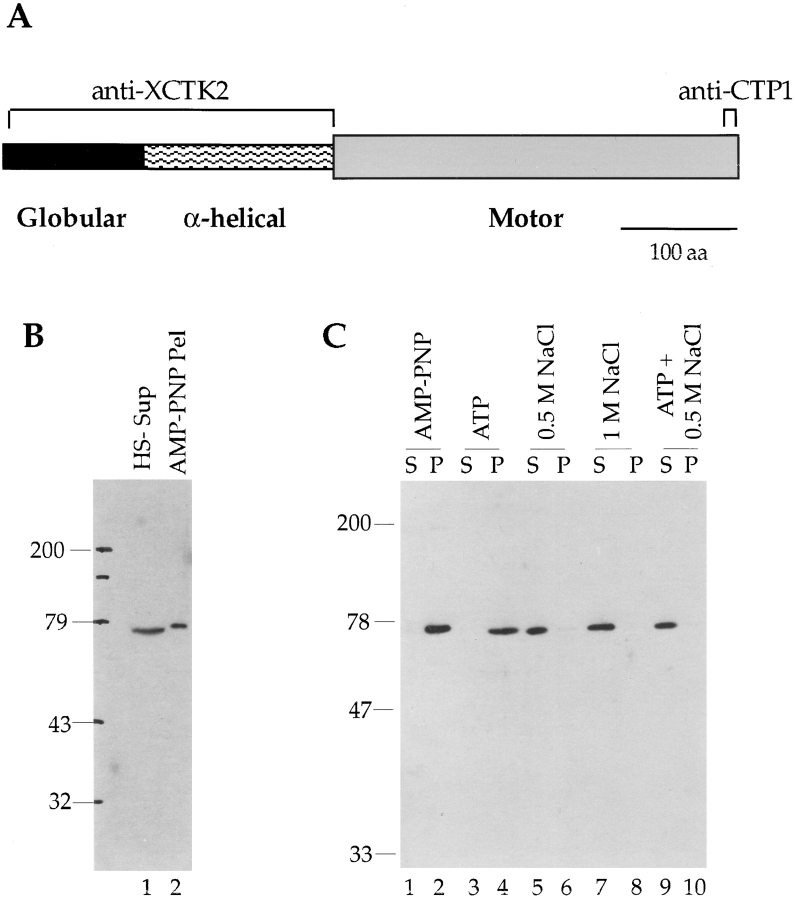
Figure 2. XCTK2 contains a COOH-terminal motor domain and binds microtubules. (A) A schematic representation of the predicted structure of XCTK2. XCTK2 contains an NH2-terminal globular domain, a central α-helical stalk and a COOH-terminal motor domain. (B and C) Immunoblots of microtubule pelleting assays in Xenopus egg extracts. (B) Xenopus egg high speed supernatants (lane 1) or AMP-PNP microtubule pellets (lane 2) were probed with anti-CTP1 antibody. The slight band shift is due to the high amounts of protein present in the high speed supernatant that alter the migration of XCTK2. (C) Microtubules were polymerized in mitotic high speed supernatants of Xenopus egg extracts and pelleted in the absence of ATP and the presence of AMP-PNP (lanes 1 and 2). The microtubule pellet, with associated proteins, was resuspended and extracted with various nucleotides and salt to generate supernatants (S) and pellets (P) of each extraction condition: 2 mM Mg–ATP (lanes 3 and 4); 0.5 M NaCl (lanes 5 and 6); 1 M NaCl (lanes 7 and 8), or 2 mM Mg–ATP with 0.5 M NaCl (lanes 9 and 10). The blots were probed with anti-XCTK2 antibody. Image published in: Walczak CE et al. (1997) Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
