XB-IMG-195571
Xenbase Image ID: 195571
|
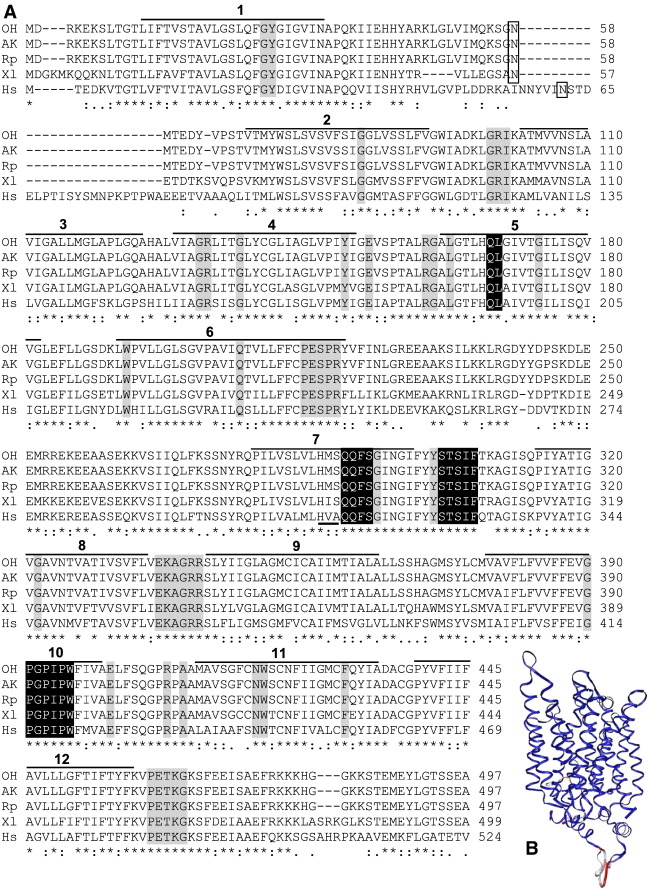
Fig. 1. Sequences of newly-identified, ranid glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) in relation to GLUTs known from other taxa. A: Deduced amino acid sequences of newly-identified GLUT2s from Ohioan Rana sylvatica (OH), Alaskan R. sylvatica (AK), and R. pipiens (Rp), aligned with GLUT2 from Xenopus laevis (Xl; accession no. NP_001084982) and Homo sapiens (Hs; accession no. NP_000331) using ClustalW in BioEdit v7.0.9.0. Gaps in the amino acid sequences are indicated with a dash (–). Amino acids that are identical (*), highly conserved (:), or moderately conserved (.) among all five sequences are identified. Box highlights a putative N-glycosylation site; horizontal bars and numbers indicate the putative 12 transmembrane regions. Amino acids that are specific to members of class 1 glucose transporters are highlighted with black; residues conserved among all GLUTs are highlighted with gray; and the HVA motif characteristic of mammalian GLUT2 is underlined [9]. B: Three-dimensional ribbon model of ranid GLUT2s, X. laevis GLUT2, and H. sapiens GLUT2 demonstrating structural alignment of multiple proteins (STAMP) tool within the Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) program. Structurally-conserved regions (blue) were found primarily within the membrane-spanning regions; whereas, less structural conservation (red) was found in the connecting loops. Image published in: Rosendale AJ et al. (2014) Copyright © 2014. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
