XB-IMG-119689
Xenbase Image ID: 119689
|
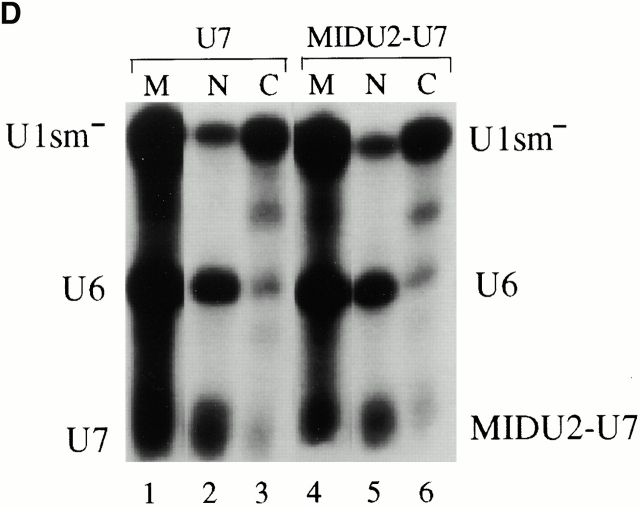
Figure 7. (A) Structures of Xenopus wild-type U7 snRNA and MIDU2-U7 chimera are shown schematically. The U7 Sm binding site is indicated by a hatched box. Thin lines represent the U7 RNA chain. In the MID U2-U7 chimera, the first 18 nucleotides of U7 are substituted with a Xenopus U2 sequence (nucleotides 19â46) indicated by a thicker line. (B) The U7 Sm binding site also supports U2 internal modification. [α32P]UTP uniformly labeled wild-type U7 (lane 1), U2-U7 chimera (MID U2-U7; lane 2), or wild-type U2 (lane 3) was injected into isolated nuclei under oil. 5 h later, RNAs were recovered and assayed for modification. The positions of uridylate and pseudouridylate are indicated. (C) Intranuclear localization of U7 and the U2-U7 chimera. 32P- and fluorescently labeled wild-type U7 and MID U2-U7 chimera were synthesized by in vitro transcription and 1 fmol of each RNA was microinjected into the nuclei of Xenopus oocytes. Nuclei were isolated 5 h later and nuclear spreads were prepared. Spreads were also prepared from uninjected oocytes as controls. DIC and fluorescence (FL) images are shown for each field. The arrowheads in the DIC panels point to Cajal bodies. Prominent Cajal body labeling was observed for both U7 and the MID U2-U7 chimera. Weak but above background nucleolar signal was also detected for the MID U2-U7 chimera. (D) The nucleocytoplasmic distribution of U7 and the U2-U7 chimera RNAs was determined as described in the legend to Fig. 4 B. Bar, 10 μm. Image published in: Yu YT et al. (2001) © 2001 The Rockefeller University Press. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
