XB-IMG-128084
Xenbase Image ID: 128084
|
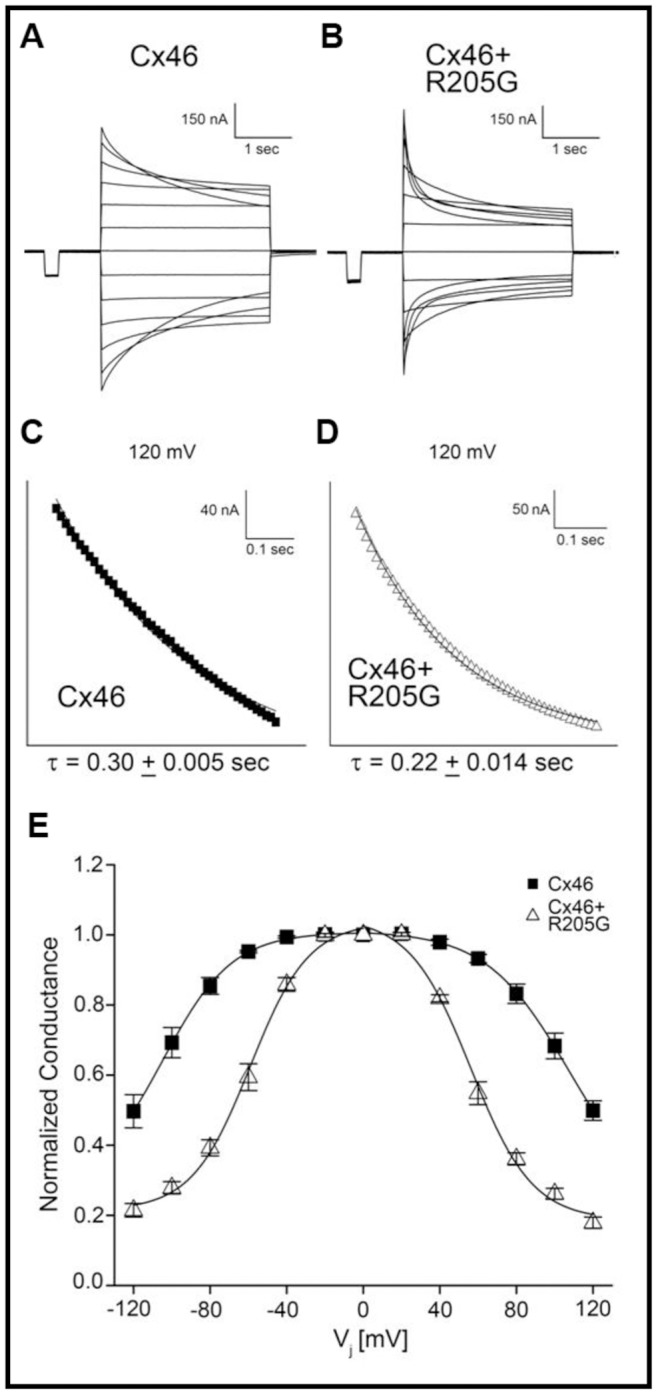
Figure 6. Voltage-gating properties of Cx46 and mixed Cx46/Cx50-R205G channels.The decay in junctional current (Ij) induced by transjunctional voltage (Vj) was plotted as a function of time for gap junctions comprised of Cx46 (A) and mixed Cx46/Cx50-R205G (B). Voltage was stepped to ±120 mV in 20 mV increments. At all voltage applications >±20 mV, mixed channels showed a more rapid current decay toward steady state. Analysis of channel closure kinetics was based on representative traces displaying the initial 250 ms of current decay recorded after application of a +120 mV transjunctional voltage, for gap junctions comprised of homomeric wild-type Cx46 (n = 5) (C) and heteromeric channels containing both Cx46 and Cx50-R205G (n = 5) (D). Current traces were fit to monoexponential decay to determine the mean time constant, τ. Heteromeric Cx46 and Cx50-R205G channels closed ∼25% faster than homomeric Cx46 channels, displaying a significant increase in mean channel closure time (p<0.05). (E) Comparison of equilibrium conductance. Steady state conductance was measured when current decay reached equilibrium, normalized to the values at ±20 mV and plotted as a function of Vj. The steady state reduction in conductance for heteromeric Cx46 and Cx50-R205G channels (n = 8) was greater than the reduction for homomeric wild-type Cx46 channels (n = 5). Image published in: Xia CH et al. (2012) Image downloaded from an Open Access article in PubMed Central. Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
