XB-IMG-121194
Xenbase Image ID: 121194
|
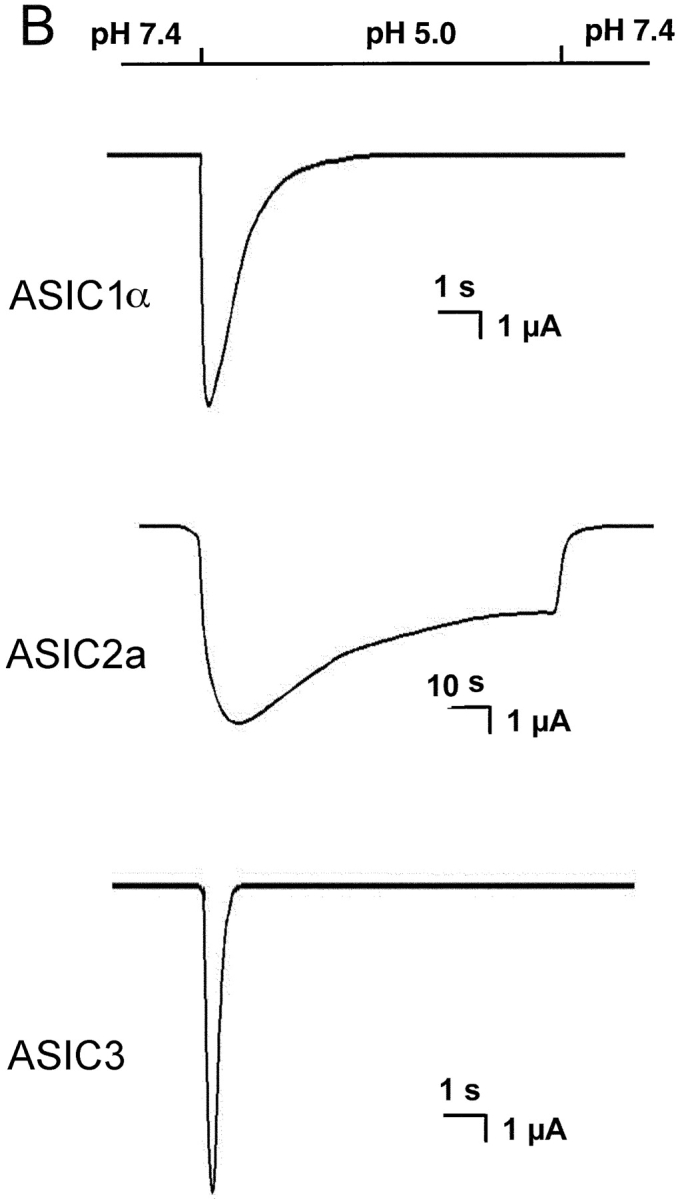
Figure 1. . (A) Representative examples of homomeric ASIC1α, ASIC2a, and ASIC3 channels recorded from outside-out patches of injected oocytes. Activation of channels was achieved by rapid changes of the solution bating the tip of the patch pipette from pHo 7.4 to 5.0 according to the protocol shown on the bar above the channel traces. The spikes in the records are noise introduced by the change in solution. The three types of channels open rapidly upon lowering the pHo to 5.0. ASIC1α and ASIC3 channels close in the continual presence of external protons, whereas ASIC2a remain open during the 5-s period of application of pHo 5.0. Recordings were performed with symmetrical 150 mM Na+, 1 mM Ca2+ in the outside solution and 0 mM Ca2+ plus 1 mM EDTA in the pipette. Membrane voltage was −60 mV in the pipette. The scale bars indicate the time and current amplitude for all the records shown. (B) Whole-cell currents from oocytes injected with ASIC1α, ASIC2a, or ASIC3 were recorded with the TEVC in the presence of 150 mM Na+ and 1 mM Ca2+ and at a membrane potential of −60 mV. Currents were activated by rapid changes in pHo from 7.4 to 5.0 as indicated by the bar above the traces. Desensitization in the continual presence of protons is faster for ASIC3>ASIC1α>>>ASIC2a. The scale bars indicate the time and current amplitude; notice that for ASIC2a the time scale is 10-fold larger. Image published in: Zhang P and Canessa CM (2002) Copyright © 2002, The Rockefeller University Press. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
