XB-IMG-124071
Xenbase Image ID: 124071
|
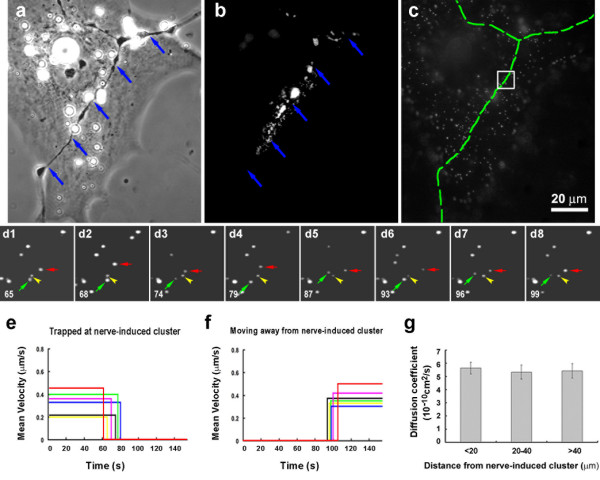
Figure 6. The effect of innervation on AChR movement. (a-c) AChR clustering at a nerve-muscle contact (blue arrows in a and b; green dashed line in c) examined with Alexa488-BTX (b) and BBQ (c). (d1–d8) Time-lapse recording of the boxed area in (c). Images were excerpted from a sequence of 130 images. The frame number is indicated at the bottom left corner of the images. Within the AChR cluster some BBQs are immobile (an example indicated by yellow arrowheads) and others are mobile (green arrows). The example of a mobile BBQ that became immobilized is shown by red arrows (trapped at frame d7). (e) The velocity plots of several BBQs at the nerve muscle contact that became immobilized. (f) Examples of trapped BBQs that resumed movement. (g) Mean diffusion coefficients of mobile BBQs at different distances from nerve-muscle contacts: 5.6 ± 0.4, 5.3 ± 0.5, 5.4 ± 0.5 × 10-10cm2/s at < 20, 20–40, and > 40 μm respectively (n = 31; error bars are standard errors). Image published in: Geng L et al. (2009) Copyright © 2009 Geng et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
