XB-IMG-126634
Xenbase Image ID: 126634
|
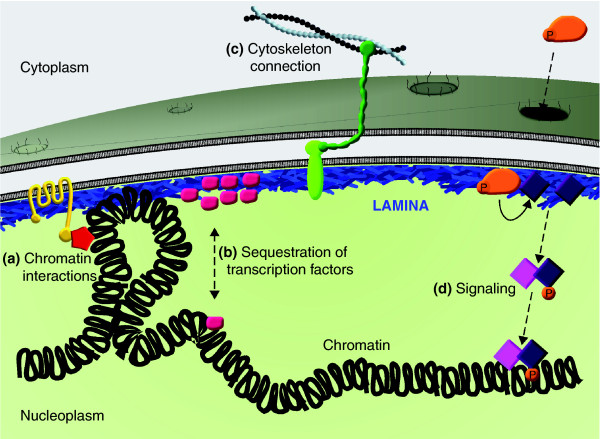
Figure 5. Functions of the nuclear lamina. A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions. (a) The lamina regulates genome organization and chromatin structure by direct interactions with chromatin and indirectly through association with chromatin-modifying and regulatory proteins. (b) The lamina regulates gene expression by sequestering transcription factors at the nuclear envelope, which limits their availability in the nucleoplasm. (c) It also mediates structural linkages between the nucleus and cytoskeleton, through the LINC complex consisting of lamins, an inner nuclear membrane protein, and an interacting outer nuclear membrane protein, which in turn binds cytoskeletal elements. (d) The lamina also provides a platform for assembly of protein complexes involved in signal transduction pathways. P, phosphate. Image published in: Dittmer TA and Misteli T (2011) Image downloaded from an Open Access article in PubMed Central. Copyright ©2011 BioMed Central Ltd. Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
