XB-IMG-125361
Xenbase Image ID: 125361
|
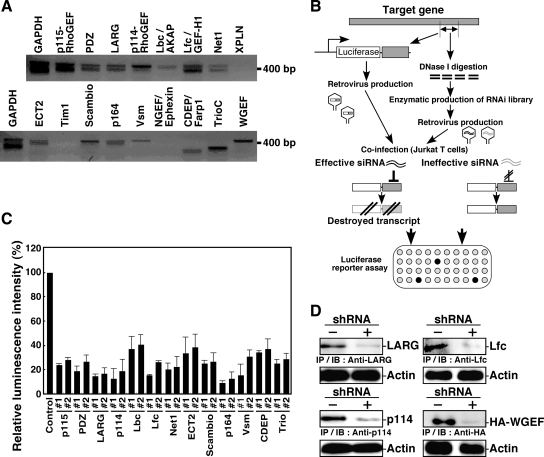
Figure 1. Screening of effective shRNA constructs targeting Rho-GEFs expressed in N1E-115 cells. (A) Expression of Rho-GEF mRNAs in N1E-115 cells. Total RNAs from N1E-115 cells were subjected to RT-PCR analysis using primers designed to amplify PCR products of ∼400 base pairs in length. Experiments were repeated twice, and similar results were obtained. (B) Schematic of the protocol for selecting effective shRNA constructs. The cDNA fragment (∼400 base pairs) of a target gene is fused to the 3′ terminus of luciferase cDNA and infected into Jurkat cells together with each individual shRNA construct from an RNAi library constructed by an EPRIL method. Effective shRNA constructs target the cognate sequences of the target gene on the luciferase-target chimeric mRNA, thus preventing luciferase expression. (C) Luciferase reporter analysis to select shRNA constructs targeting each of 13 Rho-GEFs. Jurkat cells were coinfected with retroviruses carrying a luciferase-target chimeric gene together with retroviruses carrying shRNA constructs targeting each Rho-GEF. The relative luminescent intensity for each type of shRNA-infected cells was compared with that for shRNA noninfected control cells. Data represent means ± SD of triplicate experiments. The target sequences for Rho-GEFs are listed in Supplemental Table S2. (D) Immunoblot analysis of Rho-GEF expression. N1E-115 cells were transfected with the indicated shRNA (#1) and cultured for 48 h. Expression of endogenous Rho-GEF proteins or cotransfected HA-WGEF was analyzed by immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. Actin in cell lysates was analyzed as a loading control. Image published in: Tsuji T et al. (2010) © 2010 by The American Society for Cell Biology. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
