XB-IMG-117428
Xenbase Image ID: 117428
|
|
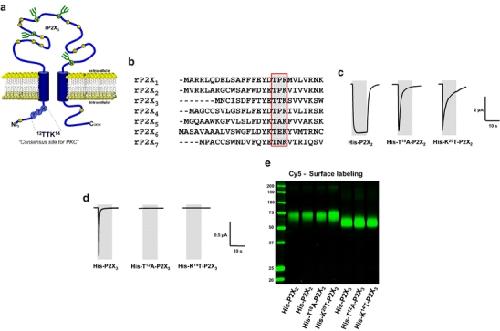
Fig. 1. Effect of site-directed modification of a putative PKC motif on currents mediated by ATP-activated P2X2 and P2X3 receptors. a Schematic model of the transmembrane topology of the rat P2X3 subunit illustrating the N-terminal position of the 12TTK14 sequence. b Alignment of intracellular N-terminal amino acid sequences of the seven P2X subunit isoforms reveals a highly conserved consensus motif, TXR/K. c Typical current traces elicited by applying 10-s pulses of 100 μM ATP to oocytes expressing the indicated wild-type or mutant P2X2 receptors. d Typical current traces elicited by applying 10-s pulses of 100 μM ATP to oocytes expressing the indicated wild-type or mutant P2X3 receptors. Gray areas indicate the duration of ATP application. e All the P2X2 and P2X3 receptors and receptor mutants were expressed efficiently at the cell surface. Intact, healthy oocytes expressing the indicated proteins for 2 days were surface-labelled with the membrane impermeant reactive Cy5 dye and then extracted with dodecylmaltoside. Recombinant proteins were isolated by Ni2+ chelate chromatography and resolved by reducing SDS-PAGE. Shown is a fluorescence scan of an SDS-PAGE gel Image published in: Franklin C et al. (2007) Image downloaded from an Open Access article in PubMed Central. © Springer Science + Business Media B.V. 2007 Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
