XB-IMG-126528
Xenbase Image ID: 126528
|
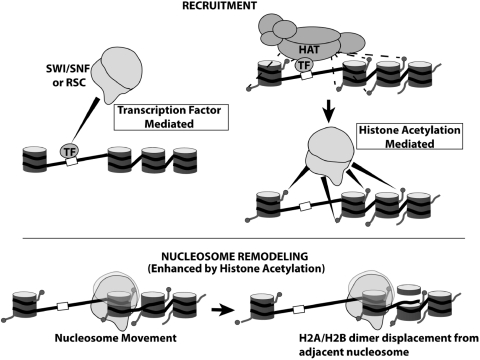
Figure 7. H3 tail acetylation modulates SWI/SNF and RSC function by distinct mechanisms. RSC and SWI/SNF recruitment occurs by two independent pathways mediated by some DNA sequence specific transcription factors (TF). Transcription activators recruit via direct interactions with SWI/SNF. Alternatively, transcription factors mediate recruitment of histone acetyl transferases (HATs) that catalyzes site-specific histone H3 tail acetylation and leads to SWI/SNF and RSC recruitment via bromodomain-acetyl lysine interaction. Recognition of acetyl marks on H3 tails via their bromodomains also modulates the nucleosome remodeling function of these complexes apart from recruitment. Specifically, H3 acetylation facilitates nucleosome movement in nucleosomal arrays and enhances H2A/H2B displacement from neighboring nucleosomes. Image published in: Chatterjee N et al. (2011) © The Author(s) 2011. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
