XB-IMG-176300
Xenbase Image ID: 176300
|
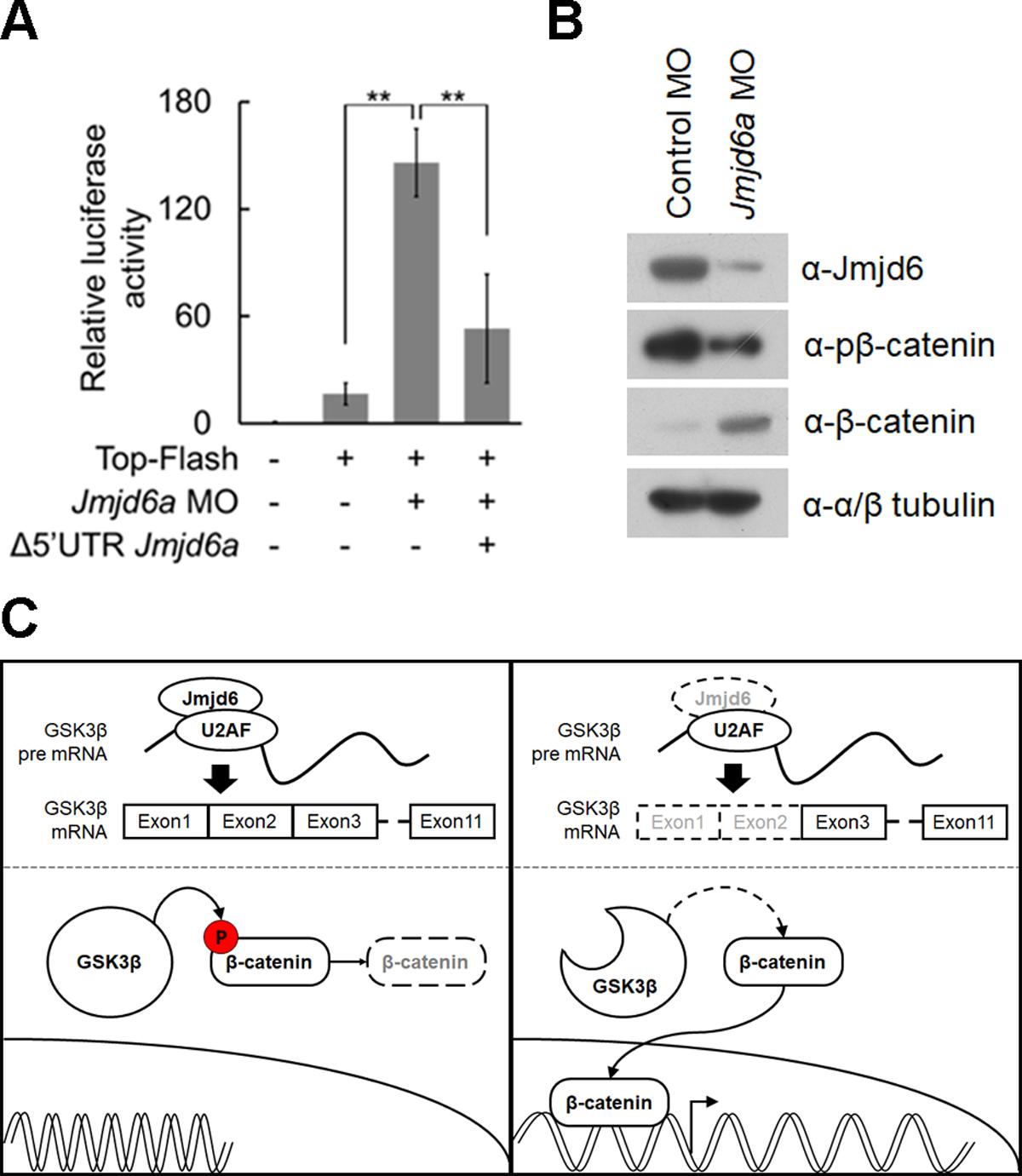
Fig 6. Altered splicing of GSK3β by Jmjd6a knockdown augments canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Xenopus laevis development.
(A) Knockdown of Jmjd6a activates canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. TOP-Flash plasmid containing TCF binding sites was co-injected with control or Jmjd6a MO into Xenopus embryos at stage 26 (n = 3). Firefly luciferase assay was performed using lysate from the anterior region of injected embryos. Renilla luciferase activity was used to normalize firefly luciferase. Over-expression of Jmjd6a (Î5âUTR Jmjd6a) suppresses up-regulation of TOP-flash activity in Jmjd6a MO-injected embryos. Data represent mean ± SD. Significance values are **P ⤠0.01. (B) Knockdown of Jmjd6a induces decreased phosphorylation of β-catenin and increased stability of β-catenin. Lysates from the anterior region of the control or Jmjd6a MO-injected embryos (stage 26) were immunoblotted with anti-Jmjd6, anti-β-catenin, and anti-phospho β-catenin (Ser33, Ser37, Thr41) antibodies (n = 3). Anti-Tubulin antibody was used as a loading control. (C) Proposed model for Jmjd6a-mediated regulation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Xenopus eye development. Image published in: Shin JY et al. (2019) © 2019 Shin et al. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
