XB-IMG-188667
Xenbase Image ID: 188667
|
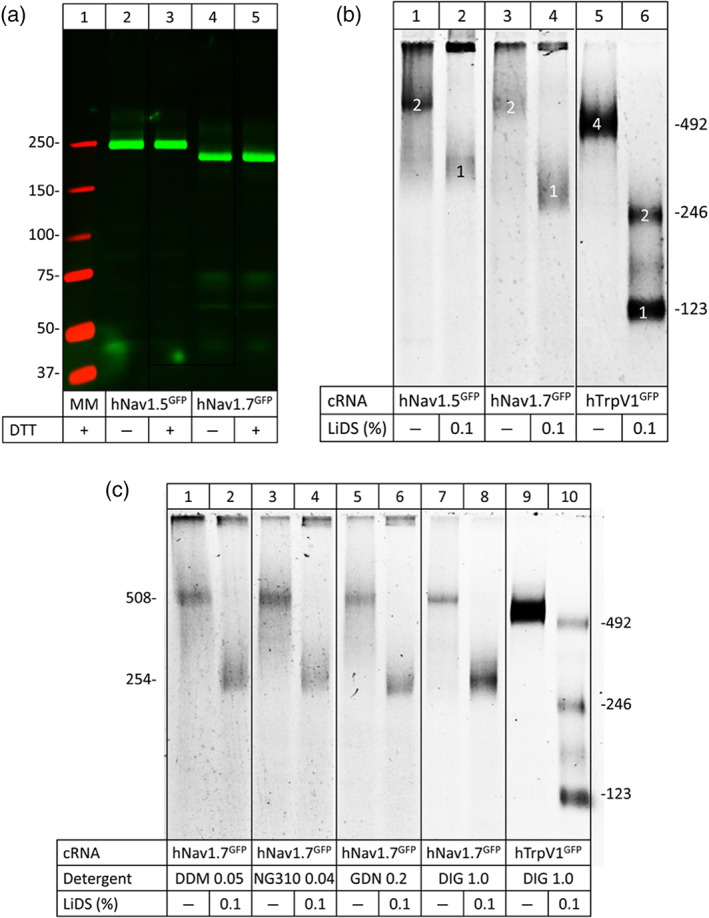
FIGURE 4. Nav1.5 and Nav1.7 migrate as nonâcovalent homodimers under native PAGE. (a) SDSâureaâPAGE of hNav1.5 and hNav1.7 in the presence or absence of the reducing agent DTT. (b) and (c) hrCNâPAGE of hNav1.5and hNav1.7 with various detergents used to turn dimers into monomers. The indicated channel proteins were extracted from Xenopus laevis oocytes with digitonin (a, b) or one of the indicated detergents (c), resolved by hrCNâPAGE, and the GFP tags were visualized by Typhoon fluorescence scanning. Protein migration is shown under native conditions and after partial denaturation (1âh incubation with 0.1% LiDS at 37°C). Numbers in the right margins in (b) and (c) indicate the sequenceâcalculated masses (protomers to tetramers) of the partially denatured hTrpV1âGFP channel. Numbers in the left margin in (c) correspond to the sequenceâcalculated masses of the hNav1.7âGFP protomer and homodimer. NG310, lauryl maltose neopentyl glycol; GDN, glycoâdiosgenin; DIG, digitonin Image published in: Rühlmann AH et al. (2020) © 2020 The Authors. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
