XB-IMG-127117
Xenbase Image ID: 127117
|
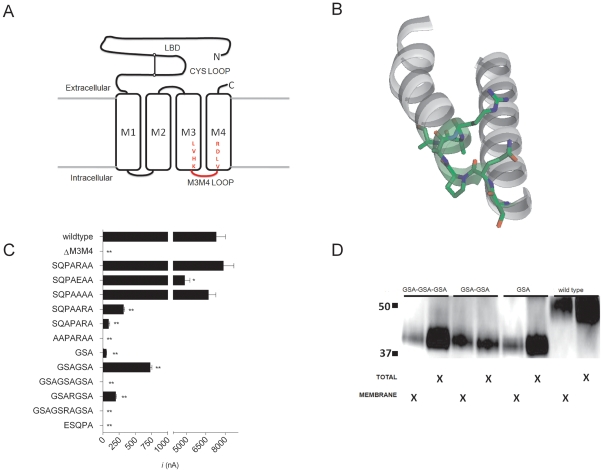
Figure 1. Construct design and initial characterization of 5-HT3A M3M4 loop truncation constructs.(A) Schematic depiction of 5-HT3A truncation constructs. The N-terminal ligand binding domain is connected to the 4 transmembrane segments (open rectangles). M1, M2 and M3 are connected by short loops. The M3M4 cytoplasmic domain including the MA α-helix have been removed and replaced with a short loop (red) corresponding to inserted amino acid linkers. LVHK and VLDR represent the terminal and initial amino acids of the M3 and M4 transmembrane domains, respectively. (B) View of the M3 transmembrane segment thru the M4 segment (including the cytoplasmic M3M4 loop) of a single subunit of the 2.9 Å high resolution crystal structure Gloeobacter violaceus GLIC protein (PDB file: 3EAM). The SQPARAA residues that were predicted to form the M3M4 loop are highlighted (green) and the side chains are shown in stick format. Note that the final three residues are part of the M4 α helix on the left. (C) Average peak current recorded from oocyctes expressing 5-HT3A-WT and 5-HT3A-M3M4 loop truncations at a saturating 5-HT (10 µM) concentration. Bars represent the mean ± SEM. The shortened cytoplasmic loops are depicted by the amino acid peptides listed. * (p<0.05) and ** (p<0.0001) indicates peak current significantly different from WT by one way ANOVA using Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc text. (D) SDS-PAGE/Western blot analysis of total and plasma membrane protein fractions from oocyctes expressing(GSA)n = 1–3 insertion constructs. 5-HT3A-V5-wild type protein (53 kDa) and 5-HT3A-V5-(GSA)n = 1–3 (41 kDa) bands are observed. Image published in: McKinnon NK et al. (2012) McKinnon et al. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
