XB-IMG-125830
Xenbase Image ID: 125830
|
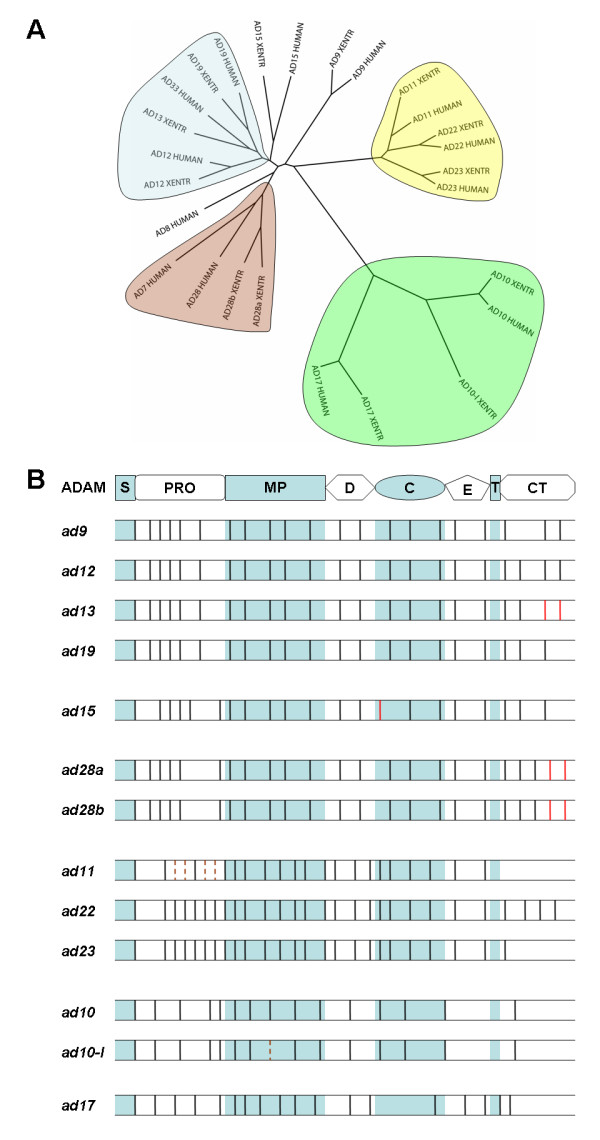
Figure 1. Phylogenetic and splicing analyses of human and X. tropicalis ADAMs. A) Phylogenetic tree of human and X. tropicalis ADAMs. Protein sequences of human and X. tropicalis (XENTR) ADAMs were aligned, and a neighbor-joining tree was drawn using ClustalX. Clades are highlighted by different colors. See Additional File 1 for an expanded phylogenetic tree including other representative vertebrate species, and Additional File 6, A-C for trees generated using alternative models. B) Comparison of splicing patterns of human and X. tropicalis adam transcripts. Splice sites within different domains (as indicated at top) of X. tropicalis adam genes, as compared with their human orthologues, are shown. Human adams 33 and 10 were used in the comparison with X. tropicalis adams 13 and 10-like (ad10-l), respectively. Black vertical lines represent splice sites that are conserved between these two species, and solid and dotted red vertical lines represent splice sites that are used by X. tropicalis adams or their human orthologues, respectively, but not both. Adam genes are divided into different subgroups (adams 9/12/13/19, 15, 28a/b, 11/22/23, 10/10-l and 17) based on their splicing patterns, as in Ref. 46. S, signal peptide; PRO, propeptide; MP, metalloproteinase domain; D, disintegrin domain; C, cysteine-rich domain; E, EGF-like domain; T, transmembrane region; CT, cytoplasmic tail. Image published in: Wei S et al. (2010) Copyright ©2010 Wei et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
