XB-IMG-124009
Xenbase Image ID: 124009
|
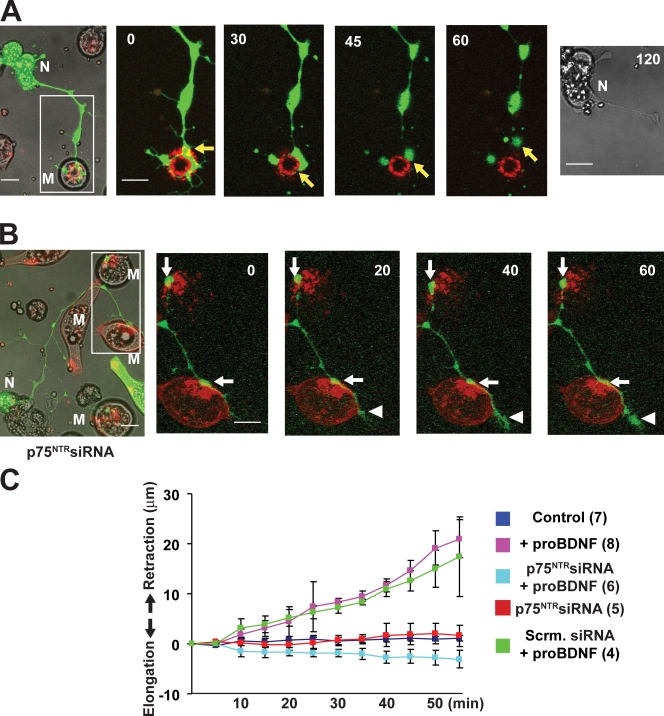
Figure 3. Pro-BDNF–induced synaptic retraction mediated by presynaptic p75NTR. (A) Time-lapse images showing the retraction of a nerve terminal from its target myocyte (M) after pro-BDNF treatment. The spinal neuron (N) is labeled with GFP (green), and AChRs on the postsynaptic membrane are labeled with rhodamine-conjugated α-BTX (red). Pro-BDNF was applied at time 0. Enlarged images of an area within the white box are shown at the left and were captured at the indicated times (shown in minutes) after pro-BDNF application. The GFP-labeled axonal terminal (yellow arrows) clearly occupied the synaptic site (colocalized with AChRs; yellow) before treatment but progressively withdrew from the junction after pro-BDNF treatment. Note that the cell body of the neuron remained healthy even after 2 h. (B) Time-lapse images showing that pro-BDNF failed to induce retraction of an axon of a neuron expressing p75NTR siRNA. Note that upon application of pro-BDNF, the terminals either did not retract (white arrows) or continued to extend further (white arrowheads). The inset is magnified to show more detailed images of the synapses. (C) Time course of synaptic retraction under different conditions. The number of experiments performed in each condition is indicated in parentheses. Error bars represent SEM. Scrm., scrambled. Bars, 10 µm. Image published in: Yang F et al. (2009) Image reproduced on Xenbase with permission of the publisher and the copyright holder. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
