XB-IMG-125584
Xenbase Image ID: 125584
|
|
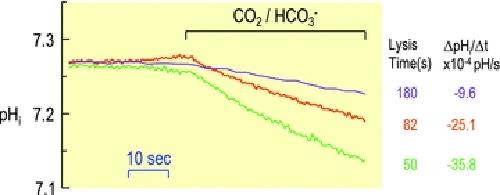
Figure 5. Effect of graded expression of human AQP1 on CO2-induced acidification rate of Xenopus oocytesThree oocytes (purple, orange and green records) injected with cRNA encoding human AQP1 were superfused with physiological saline at pH 7.5. Intracellular pH was monitored by impaling the cell with a liquid-membrane pH microelectrode and a conventional electrode for monitoring membrane potential. Data are from Cooper & Boron (1998). During the indicated periods, the extracellular solution was switched to one equilibrated with 1.5% CO2/10 mm HCO−3. The initial rate of pHi decline is an index of the CO2 permeability. After the electrophysiological recordings, the oocytes were dropped into deionized water and monitored for the time to lysis (shorter times correlating with greater osmotic water permeabilities). Together with other data, these observations showed that CO2 can move through AQP1. Image published in: Boron WF (2010) © 2010 The Physiological Society. Creative Commons Attribution license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
