XB-IMG-124142
Xenbase Image ID: 124142
|
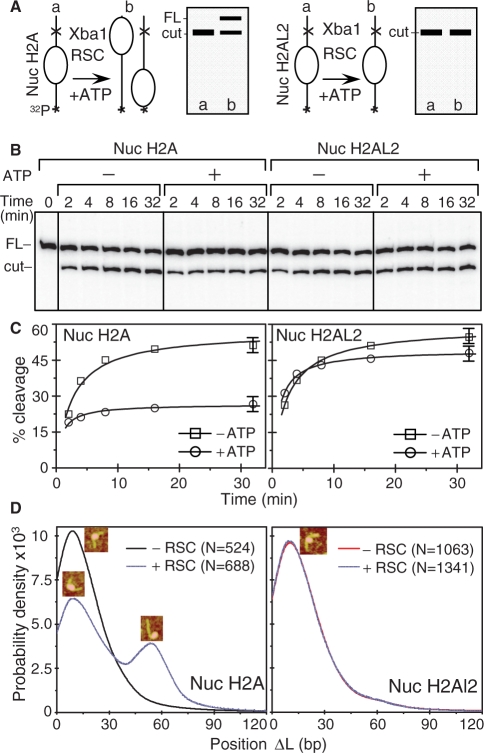
Figure 9. XbaI nuclease restriction and AFM analyses of the RSC-induced relocation of conventional and histone variant H2AL2 nucleosomes. (A) Schematics of the XbaI restriction analysis used to study the RSC-induced mobilization of conventional and histone variant H2AL2 nucleosomes. The XbaI restriction site is located in the linker DNA of the nucleosome at 233 bases from the end of the 32P-end-labeled 601.2 DNA fragment. If RSC induces sliding of the nucleosome, the cut efficiency of XbaI is expected to decrease two-fold (the nucleosome will be mobilized to both ends of the DNA fragment, left panel). If RSC is unable to mobilize the nucleosome, no decrease of the XbaI cut efficiency will be observed (right panel). (B) Identical amounts (150 ng) of H2A (left panel) or H2AL2 (right panel) 32P-end-labeled nucleosomes were incubated with 0.04 units/μl of XbaI either in the presence or the absence of 1 mM ATP. After digestion for the times indicated, the reaction was stopped and the digestion products were separated on the same 8% sequencing gel (the migrated products, which loading was not adjacent in the original gel, are demarked by vertical lines). The positions of the full length (FL) and cut DNA fragment are indicated on the left of the figure. (C) Quantifications of the data presented in (B). Note the 2-fold decrease of cut yield for the conventional H2A nucleosomes (Nuc H2A, left panel) and the absence of effect on the cut yield in the case of H2AL2 (Nuc H2AL2, right panel) nucleosomes. The digestion with Xba 1 was carried out in remodeling buffer and under these conditions a digestion plateau was reached at ∼50–60%. (D) Position distribution (ΔL) of conventional and H2AL2 histone variant nucleosomes before and after treatment with RSC. Either conventional or H2AL2 nucleosomes were treated with RSC in the presence of ATP and the samples were visualized by AFM. The insets indicate the centrally positioned (first peak) and the mobilized, end-positioned conventional nucleosomes (second peak). The numbers of analyzed nucleosomes are: N(H2A-RSC) = 524, N(H2A+RSC) = 688 conventional nucleosomes and N(H2AL2-RSC) = 1063 and N(H2AL2+RSC) = 1341 variant nucleosomes, respectively. Image published in: Syed SH et al. (2009) © 2009 The Author(s). Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial license Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
